Kanban for manufacturing: Simplifying workflow and boosting productivity
Kanban for manufacturing is a visual system that helps to control the flow of work within a process. By limiting work in progress and promoting continuous improvement, Kanban can improve workflow efficiency and reduce bottlenecks.

Henry Kivimaa

When we think about efficiency, especially related to work, we often think about Japan and, more precisely — Toyota. This car manufacturer in the beautiful island country has been one of the biggest innovators in making the most of limited resources, and it’s been a source of inspiration for many companies looking to become more efficient.
Toyota has revolutionized lean production thanks to its legendary just-in-time inventory system, which ensures that employees have just enough items on hand when they need them without excess. They also focus on developing highly efficient production lines that reduce waste and energy usage while producing high-quality products.
So, it shouldn’t be a surprise that when discussing efficient project management methodology, we again have to start with Toyota.
What is the Kanban system?

Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed the Kanban system as a lean manufacturing and project management methodology. It is a visual system that uses cards or boards to manage and control the flow of work within a process or system. Kanban means signboard or billboard in Japanese.
Kanban for manufacturing works by using a board, often a whiteboard or digital board, divided into columns representing the stages of the process. Each column represents a specific stage of the process, such as To do, In progress, and Done. Each task or work item is represented by a card, often called a Kanban card, that is moved from column to column as it progresses through the process.
The system is designed to limit work-in-progress and ensure work is completed efficiently and effectively. By limiting the amount of work that can be in progress at any one time, the Kanban system helps to reduce bottlenecks and improve workflow. The system also promotes continuous improvement by encouraging teams to identify and resolve problems as they arise.
Kanban is widely used across various industries and has been adapted to many different processes and systems. It is particularly popular in software development, project management, and manufacturing but can be applied to almost any process involving a workflow.
For our purposes, the focus will remain on manufacturing, so let’s explore in more detail what is Kanban in manufacturing.
What are the 3 main types of Kanban?
There are different types of Kanban cards that can be used, including:
- Production
- Withdrawal
- Transportation
- Supplier
- Emergency
Let’s look at the three main ones.
Production Kanban
This type of Kanban signals to the previous process that a specific quantity of parts or raw materials is required for production. When the materials are consumed, the production Kanban is sent back to the supplier process, indicating that more materials are needed.
Withdrawal Kanban
This type of Kanban signals to the next process that the required parts or materials are ready to be used. When the parts are withdrawn from the previous process, the withdrawal Kanban is sent back to the supplier process, indicating that more parts are needed.
Transportation Kanban
This Kanban manages the movement of materials between processes or locations. The transportation Kanban signals the need to move materials from one location to another, ensuring that materials are delivered to the correct location at the right time. This type of Kanban is critical for organizations with multiple warehouses or production sites, as it ensures that materials are available where and when they are needed, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
Each of these Kanban types plays a specific role in managing the flow of materials and information in the production process. Using Kanban to create a pull-based system makes the production process more efficient, with materials and parts being produced only when needed, reducing inventory levels and minimizing waste.
What is Kanban in lean manufacturing?
In lean manufacturing, Kanban is used to manage the flow of materials and information throughout the production process. Each Kanban card represents a specific product or part, and the card is used to track the status of that item through the production process.
As each item is produced and moved to the following process, the Kanban card is moved with it to indicate that the item has been consumed and that more production is needed.
The Kanban system is designed to be simple and flexible and can be adapted to various manufacturing processes. It is based on the principle of visual control, which means that the production status is easily visible and understandable to all workers. This enables workers to quickly identify any issues or bottlenecks in the production process and take action to resolve them.
In addition to its benefits for production efficiency and waste reduction, Kanban promotes continuous improvement and teamwork. The Kanban system fosters a culture of collaboration and problem-solving by enabling workers to see the production status and work together to resolve issues.
Overall, Kanban is an essential component of lean manufacturing and a powerful tool for improving production efficiency, reducing waste, and promoting continuous improvement.
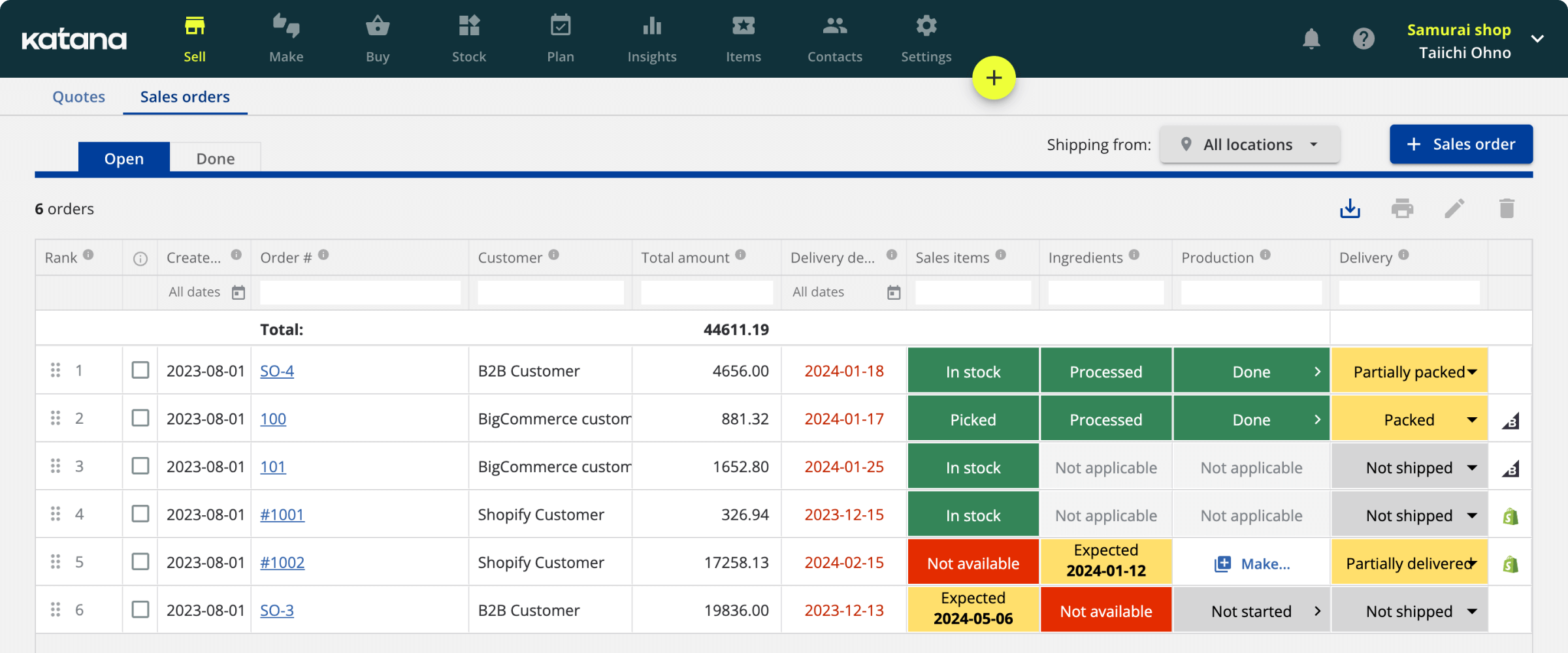
Manufacturing Kanban board example
To better understand what a lean Kanban board looks like, we’ve created this example of Kanban in lean manufacturing.
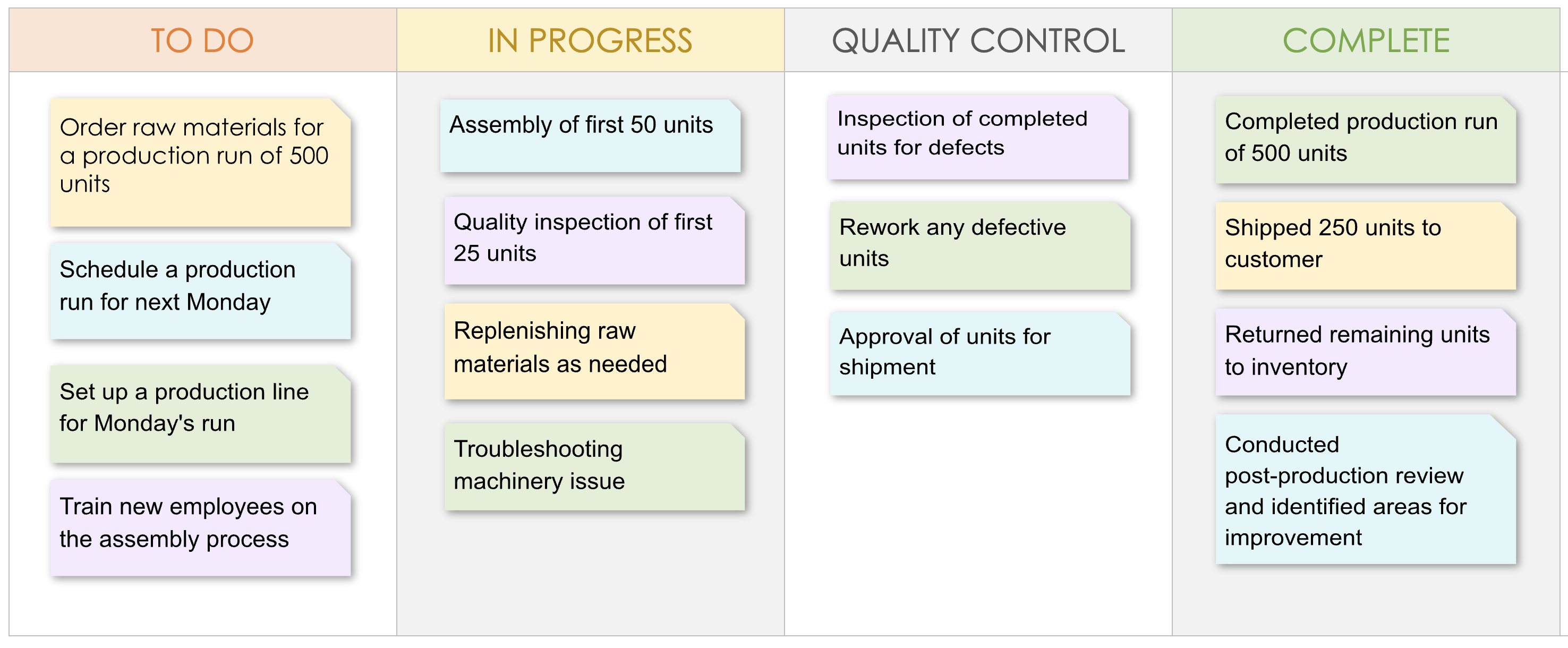
Each task on the Kanban board is represented by a card or sticky note that moves through the various columns as it progresses through the automotive manufacturing process at Toyota. The Kanban board provides a visual representation of the status of each task, allowing the team to see what needs to be done, what is currently in progress, what needs quality control, and what has been completed.
The movement of the cards or sticky notes between columns indicates the progress of each task and allows the team to see which tasks need attention and which are completed. The Kanban board is an effective tool for managing the manufacturing process and ensuring that each task is completed efficiently and effectively.
Pros of using Kanban for manufacturing
There are several potential benefits to using Kanban for manufacturing. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved efficiency — Kanban in manufacturing can help improve the efficiency of the manufacturing process by reducing waste, minimizing lead times, and optimizing inventory levels. By focusing on the flow of work and using visual signals, Kanban can help identify bottlenecks and other areas of improvement.
- Better communication — Kanban for manufacturing promotes better communication between different teams and departments within the manufacturing process. This can help ensure everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals. Kanban in production helps to reduce confusion and misunderstanding by providing a clear picture of what needs to be done and when.
- Increased flexibility — Flexibility and adaptability are the key characteristics of Kanban systems, enabling them to effectively accommodate changes in demand, production requirements, and other factors that may affect the manufacturing process.
- Reduced inventory costs — Using a pull-based system that only produces what is needed, Kanban can help reduce carrying costs and minimize waste. This can help to improve profitability and reduce the risk of overproduction.
- Continuous improvement — Kanban systems are designed to promote continuous improvement by encouraging teams to identify areas where advancements can be made and then implementing changes to address those issues. This can help ensure that the manufacturing process always evolves and improves over time.
Clearly, there are a lot of pros, but let’s also look at the other side of the coin — the challenges.
Want to see Katana in action?
Need software built for manufacturers that tracks all four types of inventory, manages production processes, assigns tasks to shop floor, and integrates with other business tools you use? Look no further.
Challenges of using Kanban for manufacturing
While Kanban systems can bring many benefits to manufacturing processes, there are also some challenges that organizations may face when implementing them. Here are a few examples:
- Initial implementation — The implementation of Kanban systems can be complex and time-consuming, particularly if the manufacturing process is already established. This may require significant changes to existing workflows and procedures, and employees may need to be trained on the new system.
- Lack of understanding — Kanban systems rely on the understanding and cooperation of all employees involved in the manufacturing process. If employees do not fully understand the system or are resistant to change, it can hinder the system’s effectiveness.
- Complexity of the process — Depending on the complexity of the manufacturing process, implementing Kanban systems may be more difficult or less effective. For example, multiple-stage processes may require more sophisticated approaches to managing inventory effectively.
- Lack of standardization — Kanban systems require standardized processes and materials to function effectively. If there are inconsistencies or variations in the manufacturing process, it can be difficult to implement Kanban systems that work consistently across all stages of production.
Overall, while Kanban systems can bring many benefits to manufacturing, organizations should carefully consider these and other potential challenges before implementing them.
7 tips for implementing Kanban for manufacturing

If you’ve mulled over the challenges and decided to go ahead with implementing Kanban for your manufacturing plant, here are 7 tips you can follow to make this process as effortless as possible.
- Define your process — You need to define your manufacturing process and identify where waste and bottlenecks occur. Map out your process flow, and identify areas where Kanban for manufacturing can help improve flow and eliminate waste.
- Start small — Implement Kanban for manufacturing in a small area or process before rolling it out across your entire facility. This way, you can test and refine your strategy and identify any issues before they become too widespread.
- Set limits — Establish limits for each Kanban card or container, such as maximum inventory levels or lead times. This helps you prevent overproduction and ensure that your production line stays balanced.
- Use visual signals — Cues such as color-coded cards or bins help indicate when inventory needs to be replenished or when production needs to be slowed down or stopped. This makes it easy for your team to understand what they need to do.
- Train your team — Provide training to your team members on how to use the Kanban system effectively and ensure that everyone understands the process and their roles within it.
- Continuously improve — Regularly review and evaluate your Kanban process to identify areas for improvement. Use metrics such as cycle time, lead time, and inventory levels to track your progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Embrace a culture of improvement — Kanban is a tool for continuous improvement, and it’s vital to foster a culture of continuous improvement throughout your organization. Encourage your team members to suggest enhancements and use their feedback to refine your process and make it even more effective.
Upgrade from Kanban to an inventory management system
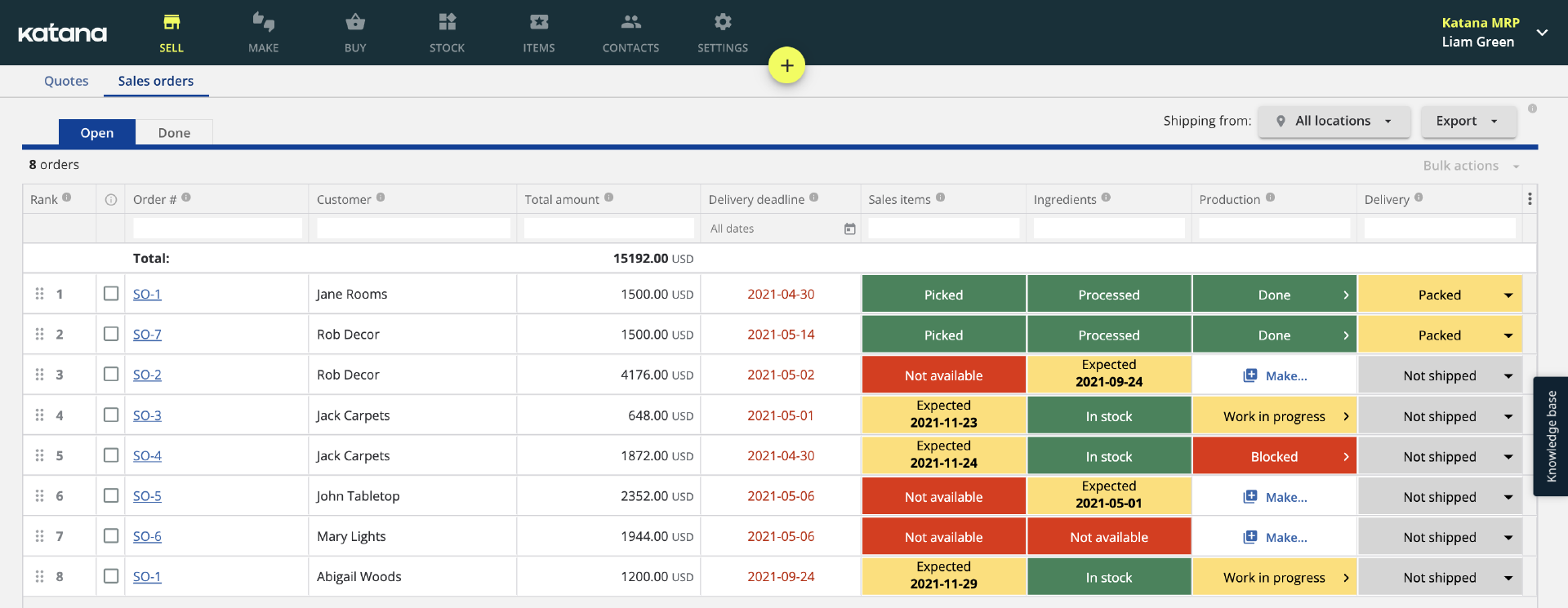
Kanban boards are great for managing workflows and providing a clear visual overview of ongoing tasks. However, if you’re looking to take your process organization and inventory tracking to the next level, it may be time to upgrade from Kanban boards and invest in an inventory management system.
Katana’s live inventory management software provides real-time data about your stock levels, cost of goods sold (COGS), shop floor operations, and more.
With Katana, your stock levels are updated in real time whenever a new order is generated so that you can stay on top of your inventory. You can also set reorder points in Katana and get notified when items run low, making it easy to avoid stockouts.
To ensure a unified user experience, Katana offers seamless integrations with the best business tools out there, including:
Having all your business tools synchronized eliminates a lot of tedious admin, saving you and your employees a lot of time.
Get started by booking a demo to see how Katana can help you upscale your business.

Henry Kivimaa
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control