Digital manufacturing: A new way to work
Digital manufacturing is the ultimate tool for manufacturers looking to take control of their entire business.

James Humphreys

Decades ago, when companies were trying to build a manufacturing production facility, they would be limited by the product they were designing.
It generally needed to be complete, with a working prototype, before decisions could be made on how to best construct and lay out an assembly line, what machines would be used, or how to configure the process. This was an expensive and time-consuming undertaking that could take months or even years before yielding any actionable results.
Today, after a digital transformation for manufacturing, companies can build a complete virtual model of their facility and assembly process before any physical prototype is created. Engineers can work out kinks in the design and perfect the manufacturing process before a single item is produced. This speeds up development timelines and reduces costs by allowing errors to be corrected early on.
Below, we’ll dig into what digital manufacturing is based on, the methods, the benefits a company might receive, and how it might be used in different industries.
What is digital manufacturing?
Digital manufacturing is the process of using technology to create a virtual model of a product or process before it is physically created. Based on the principles of Industry 4.0, engineers can test and iterate on the design before any resources are committed to production.
It also makes it possible to create custom products on demand without requiring large minimum order quantities or inventory management. This is because the product can be produced only when it is ordered, and there is no need to keep finished goods on hand.
This technology-driven approach is made possible by advances in 3D printing, computer-aided design (CAD), and manufacturing execution systems (MES).
By connecting these tools and using them to create a digital twin of the manufacturing process, companies can map out every step of production before a physical product ever exists.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
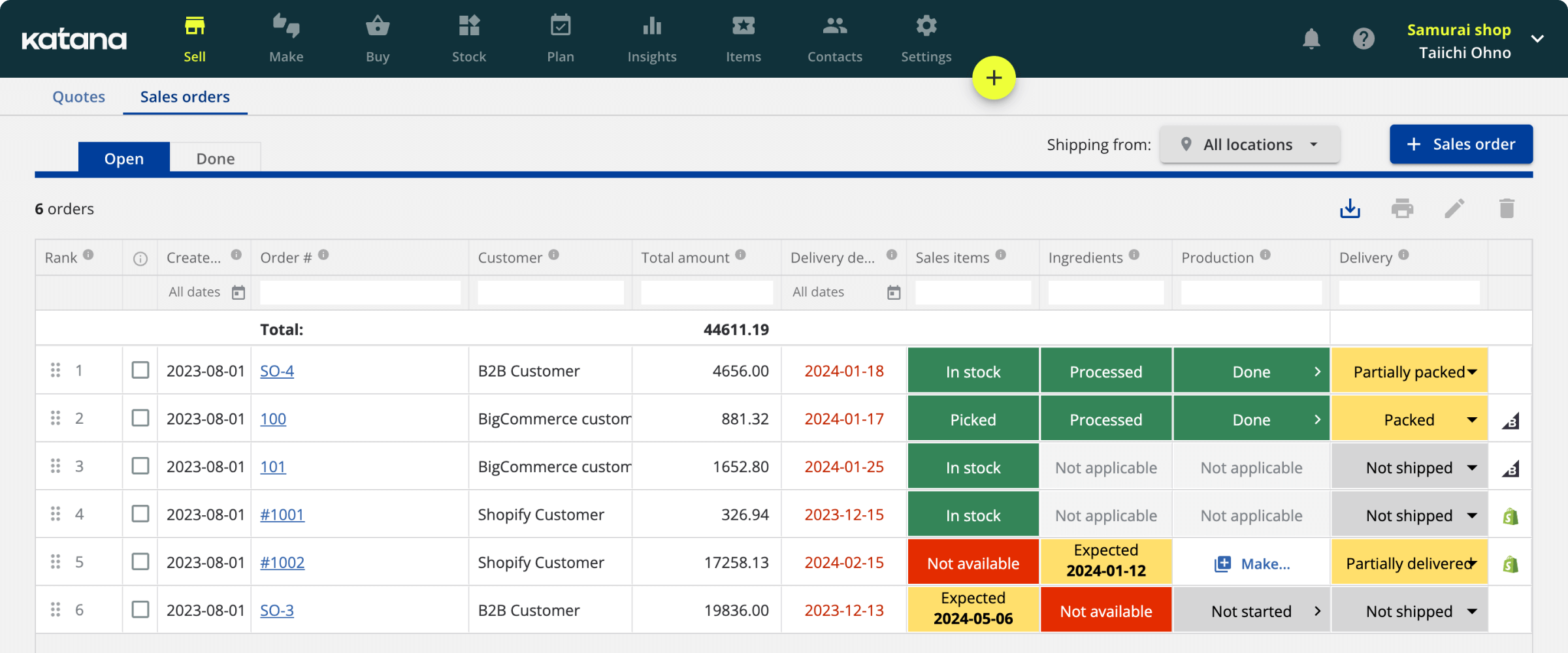
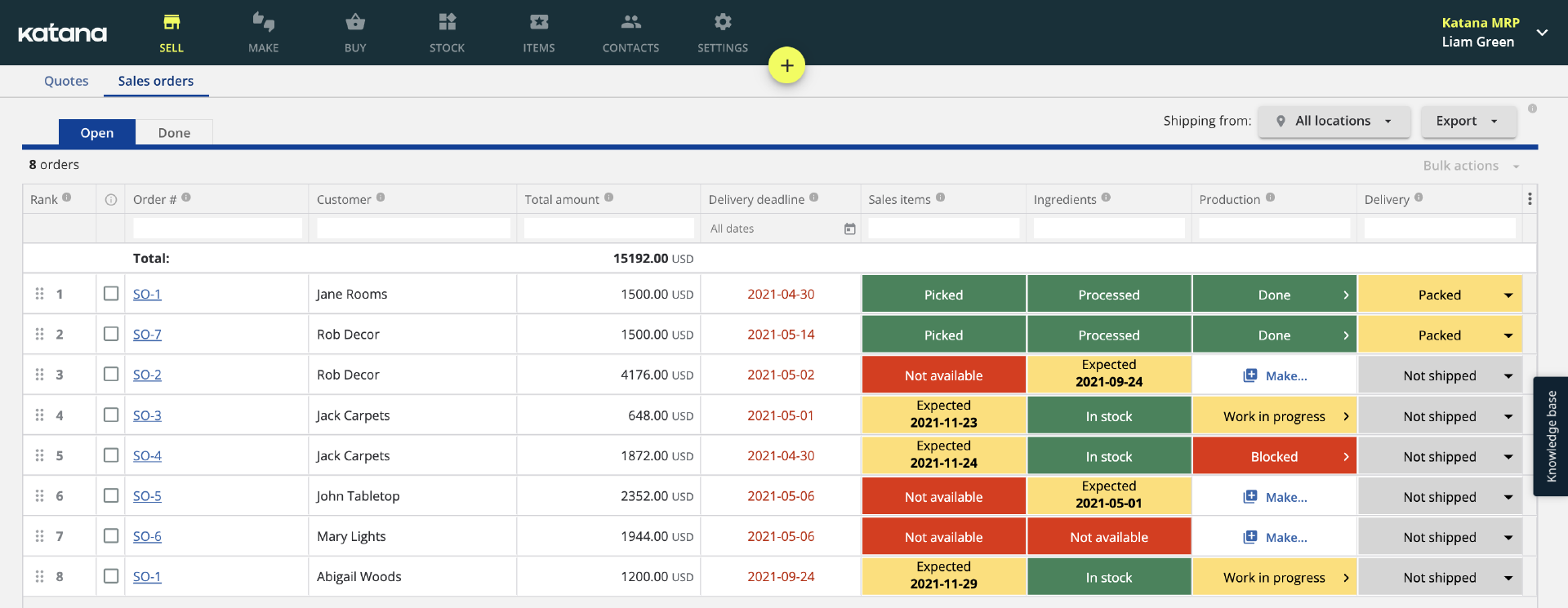
With an enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution, these processes can be automated and further streamlined.
By integrating all of the data from different machines and processes into a single system, decision-makers can get a complete picture of the manufacturing process and make real-time changes as needed. This also enables companies to track inventory levels and predict when they will need to order more raw materials. In the past, this information was often siloed in different departments or on separate systems, making it difficult to get an accurate overview of the manufacturing process.
ERP systems can help to close those gaps and give everyone on the production team a clear view of what is happening at every stage.
Computer-integrated manufacturing
At its core, digital manufacturing is about using technology to improve the efficiency of the production process.
This is done by connecting different machines and systems to share data and information. This is known as computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM). Integrating the machines in a factory makes it possible to track production in real time and make adjustments on the fly if there are any issues.
For example, if one machine in the assembly line is running slow, the CIM system can automatically reroute work to another machine to keep production moving.
This flexibility and agility is impossible with a traditional, linear assembly line.
Another benefit of CIM is that it makes it easier to change or update the manufacturing process. The digital model can be quickly updated and sent to the machines if a new product is introduced. This eliminates the need for retooling and reduces downtime between different production runs.
Product lifecycle management
Product lifecycle management (PLM) is another key element of digital manufacturing.
PLM software is used to manage the data and files associated with a product, from its initial design to its eventual retirement. This includes all the information about the materials, components, and assembly processes required to create it. By readily making this information available, companies can more easily make changes to the product or process.
For example, if a supplier discontinues a material, the PLM system can quickly identify and select a suitable replacement. This helps to avoid production delays and keeps the manufacturing process moving forward.
Another benefit of PLM is that it provides a central repository for all the product data. This makes it easy for different teams within the company, such as engineering, manufacturing, digital marketing, and sales, to access the information they need.
It also helps to ensure that everyone works with the most up-to-date files, which can avoid costly mistakes.

Benefits of the digital manufacturing
Digital manufacturing offers many benefits for companies, including:
- Reduced development time and costs — Companies can save time and money by testing the design and manufacturing process before any physical prototype is created. This is because potential problems can be identified and corrected early on before they cause delays or require expensive rework
- Increased flexibility — The ability to quickly change the design or process as needed provides greater flexibility for companies. This can be a major advantage when responding to customer feedback or market changes
- Improved quality — By having a complete understanding of the manufacturing process before any physical product is created, companies can avoid potential errors and produce a higher-quality product
- Greater customization and personalization — Running simulations on a product and its creation for a specific customer opens up new opportunities. This can be used to create unique products or to tailor the manufacturing process to the needs of a particular client
- Enhanced collaboration — Using digital technologies such as CAD and PLM software can help improve collaboration between different teams within the company. This is because everyone has access to the same product data and files, which can avoid confusion and mistakes
- Marketing integrations — Manufacturing digital marketing can be difficult to master. With a technology-based design and engineering process, companies can have a better understanding of how their product is being made and can use this information to create more accurate marketing materials
As technology becomes more complex and your customers’ needs more sophisticated, keeping up with the industry’s best practices is critical for business success.
Katana digital manufacturing software
Katana is a cloud-based digital manufacturing software that empowers users to take control of their entire business from a single platform — giving you purchase, sales, shipping, and operations management at your fingertips.
Leveraging digital manufacturing in your own company
If you are already up and running with a physical production line, it can be difficult to see the benefits of creating a digital workflow. However, there are several ways that you can leverage digital manufacturing in your own company:
- Enhanced prototyping — If you have a new product design that you want to test, consider using digital manufacturing to create a virtual prototype. This will allow you to make changes as needed and get feedback from potential customers before committing to the design
- Custom offerings — As digital manufacturing allows for greater customization, you can use it to create unique products for your customers. This could be anything from personalized gifts to bespoke items that are not available anywhere else
- Shorter runs — If you need to produce a small number of items for a specific customer or project, digital manufacturing can be a great option. This is because you can create a single item or a small batch without incurring the same costs as a traditional production run
Digital manufacturing is a powerful tool that can help companies to speed up development, reduce costs, and improve quality. It is based on the latest technology advances and offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for businesses.
Choosing an ERP solution offering digital manufacturing integration is a good first step. This allows you to manage all aspects of your production line in one place and take advantage of the many available benefits.
Thousands of manufacturers have used Katana to build better businesses. Get started by booking a demo with Katana today.

James Humphreys
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control