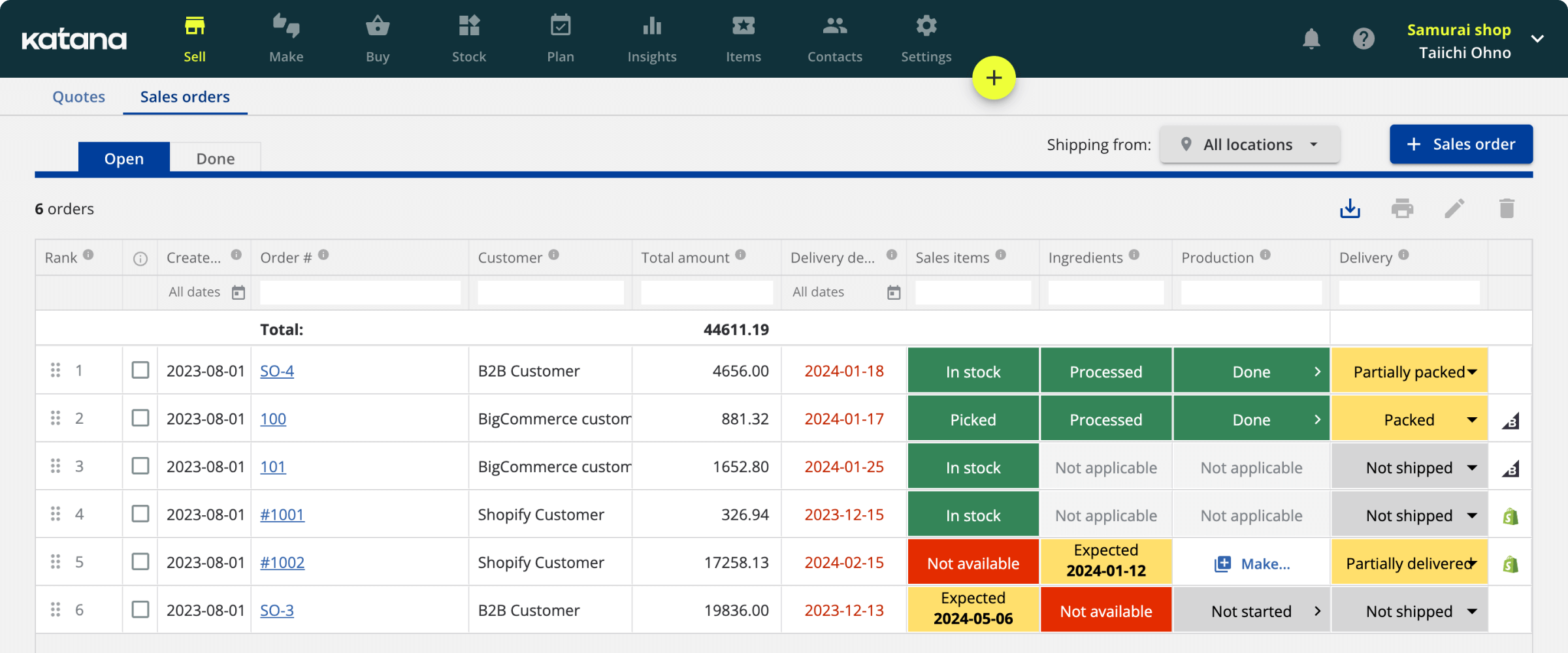
19 electronics manufacturing process challenges and solutions
Without careful vigilance, it’s easy for electronic components to become outdated or acquire defects. This article looks into all the challenges those working in the electronics manufacturing industry face and how they can fix them.

James Humphreys
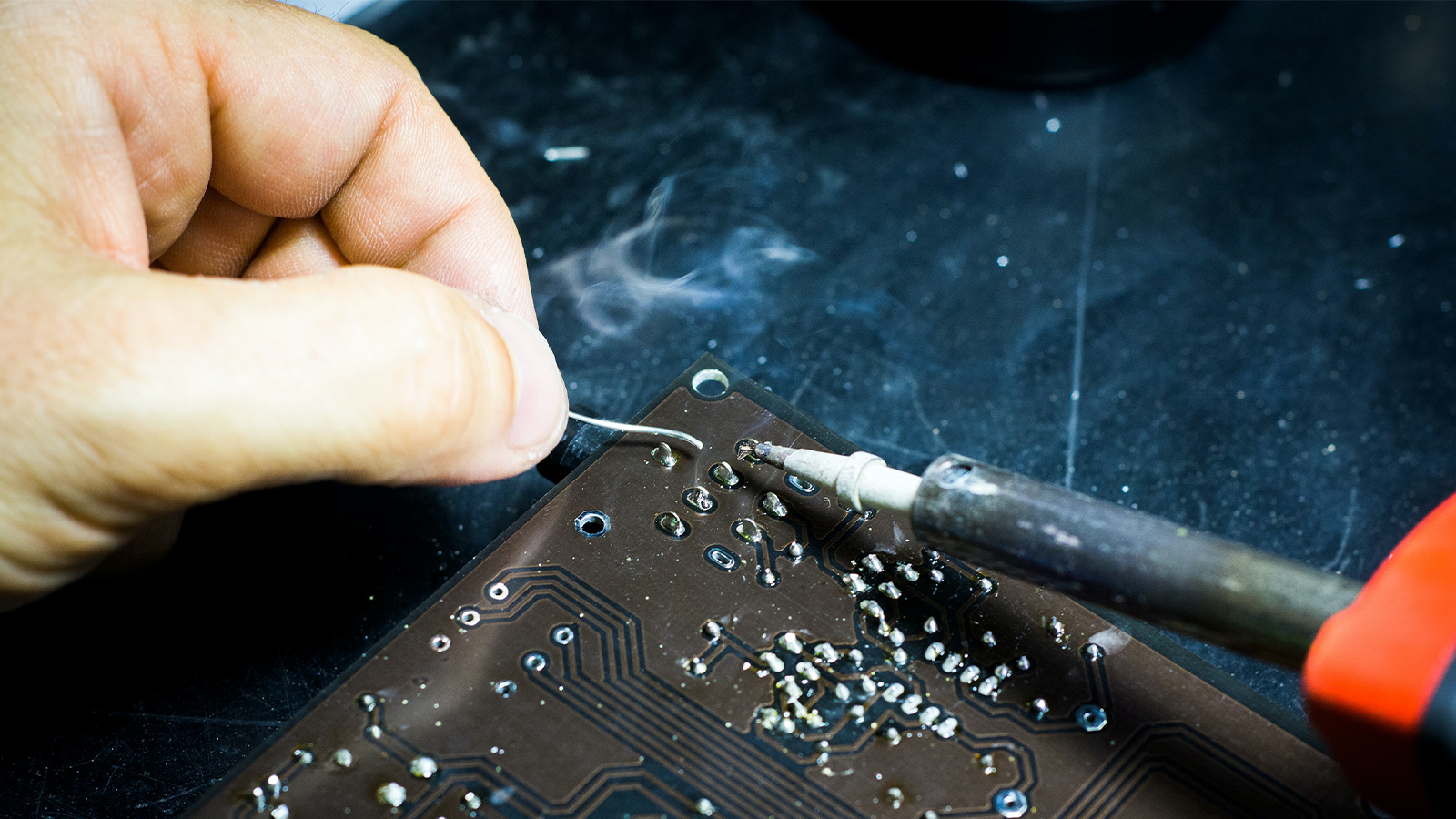

According to comedian and actor Jim Carrey, the zombie apocalypse came in the form of us all being glued to our phones.
Regardless of whether you find this observation a bit dramatic, he’s not wrong about the popularity of cell phones. In 2021 Pew Research Center looked into cell phone ownership in the US and found that 97% of Americans own a cell phone¹. This highlights just how influential the electronics industry is in our lives. And this trend doesn’t seem to be slowing down, especially in the United States.
According to the US Department of the Treasury, the US has seen a meteoric rise in spending on the construction of manufacturing facilities². This is mainly driven by construction for computer, electrical, and electronic manufacturing, indicating the growing significance of these sectors in the overall manufacturing landscape.
That’s why we’ve decided to look into the electronics manufacturing process, the challenges, and the ultimate solution to managing these products.
What is electronics manufacturing process in production?
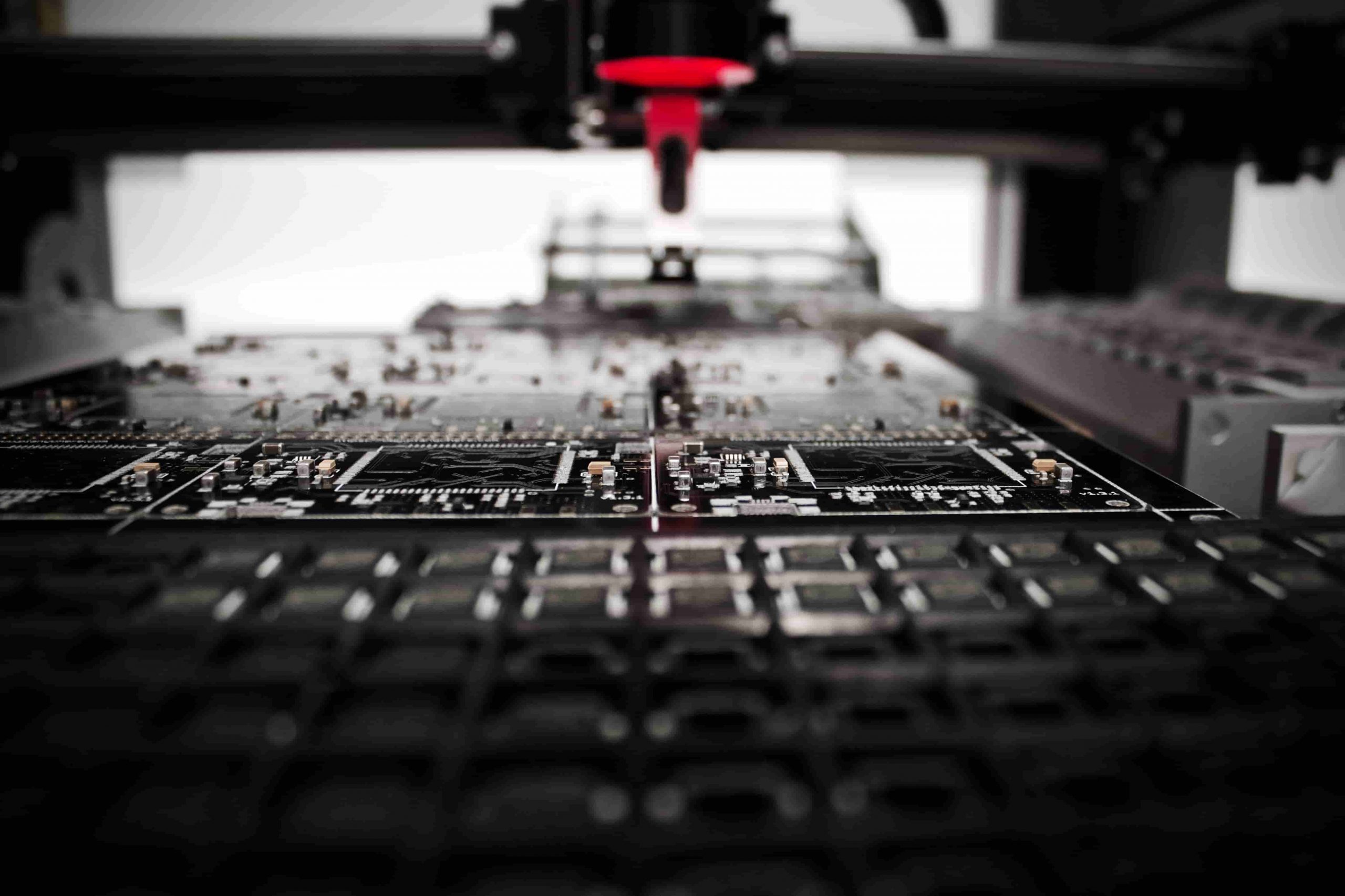

The electronics manufacturing process in production is the methodology manufacturers use to transform design concepts into tangible electronic products. It encompasses various stages such as design, component sourcing, assembly, testing, enclosure manufacturing, quality control, and packaging.
Let’s take a closer look at each step of this process.
1. Design and prototyping
The initial step is designing the electronic product and creating a prototype. This involves conceptualizing the product, designing the circuitry, and creating a prototype for testing and refinement.
2. Component sourcing
Once the design is finalized, the necessary electronic components are sourced from suppliers. These components can include integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, connectors, and various other parts required for the product.
3. PCB assembly
The printed circuit board (PCB) is fabricated, and the electronic components are mounted onto it through a process called PCB assembly. Surface mount technology (SMT) is commonly used for this, where the components are soldered onto the PCB using automated machines.
4. Testing
After the PCB assembly, the electronic product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure its functionality, performance, and adherence to quality standards. Various tests, such as functional testing, environmental testing, and reliability testing, may be conducted.
5. Enclosure manufacturing
The product’s enclosure or casing is manufactured, which provides physical protection and houses the electronic components. Enclosures can be made of plastic, metal, or other materials, and they are often designed to be aesthetically appealing.
6. Final assembly
The PCB, along with other components such as displays, buttons, connectors, and cables, is integrated into the enclosure. This stage involves the final assembly of the electronic product.
7. Quality control
Quality control processes are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each product meets the required standards. This includes consulting the production quality control checklist and performing inspections, testing, and quality assurance checks at different stages.
Download your free production quality control checklist
Quality control is crucial when it comes to electronic components manufacturing. Download this free quality control checklist and ensure all your products meet the highest standards your customers expect.
8. Packaging and shipping
Once the electronic products have passed quality control, they are packaged appropriately for shipment. Packaging materials protect the product during transportation and include boxes, manuals, cables, and any other accessories. The products are then shipped to wholesalers, distributors, retailers, or directly to customers.
It’s important to note that the exact manufacturing process can vary depending on the complexity of the electronics being produced and the specific industry practices.
Eco-friendly initiatives
The current manufacturing trends and predictions indicate a significant shift in consumer focus. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of minimizing their environmental impact, leading to a growing emphasis on adopting sustainable practices in electronic product manufacturing.
Many businesses are striving to become green manufacturing companies, prioritizing environmentally friendly approaches. For instance, some assembly plants have embraced solar power as a renewable energy source to power their operations. By harnessing solar energy, these plants can reduce emissions and conserve energy, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
The electronics manufacturing process is an important part of the global economy. It provides jobs for millions of people and creates products that we use every day. As consumers, we should be aware of how our devices are made and their impact on the environment. We can all play a role in ensuring that the process is as eco-friendly as possible.
Preparing your workspace for PCB handling
Printed circuit board assemblies, or PCBs, are thin boards made of various materials used to support and connect electronic components — the PCB assembly process is an important and delicate stage in making electronic goods.
They are found in various electronic devices, from computers and cell phones to televisions and microwaves. If you are working with printed circuit boards (PCBs), it’s essential to take proper precautions to avoid damage. Here are some tips on how to prepare your workspace for PCB handling:
- Make sure the area is clean and free of debris to ensure PCB quality
- Cover any sharp edges on tables or other surfaces
- Use static-free mats or workbenches if possible
- Wear gloves to avoid fingerprints or other marks when handling the boards
- Avoid touching the exposed circuitry on the boards during fabrication and PCB assembly
These simple tips will help ensure that your PCBs stay in good condition, last for many years, and stay relevant in the electronics manufacturing industry.
Whether you’re handling the PCB fabrication or outsourcing the process, following these tips will ensure that you’re handling your boards safely.
What is PCB layout design for manufacturability?
Design for circuit board manufacturability (DFM) is the process of organizing PCB layout topology to mitigate problems during fabrication and assembly. Good DFM considers many factors, from component placement and routing density to thermal management and signal integrity.
PCB designers must balance meeting electrical performance requirements and ensure that their boards are manufactured within budget. DFM helps to streamline the design for the manufacturing process and minimize manufacturing costs by identifying potential issues early on.
There are many different approaches to DFM, but some common considerations include:
- Component placement — Components should be placed to minimize interactions between signals. This can help to reduce crosstalk and other forms of signal noise.
- Routing density — Higher routing densities can lead to problems with etching and soldering. PCB design guidelines should aim for a balance between dense routing and clearances that allow for manufacturing tolerances.
- Thermal management — Temperature gradients can cause components to expand or contract unevenly, leading to reliability issues. Proper thermal management ensures that components stay within their safe operating temperatures.
- Signal integrity — High-speed signals are susceptible to crosstalk and other forms of signal degradation. Good DFM practices help to ensure that signals maintain their integrity throughout the PCB.
PCB layout is a critical part of the product design process, and DFM helps optimize the layout for manufacturability. Electronic designers can create PCBs that are both easy to manufacture and meet electrical performance requirements by considering a wide range of factors.
PCB boards
PCB manufacturers produce different types of PCB boards. When looking for PCB designs, make sure you’re purchasing the correct board for your product. The common types of PCB boards are:
- Single layer with a copper layer
- Copper PCB
- Heavy copper PCB with hole components
- Multilayer PCB
- HDI PCB
Electronics manufacturing outsourcing
Outsourcing electronics manufacturing has become a common practice in the industry, offering numerous benefits to companies seeking cost-effective and efficient production solutions. Let’s go over some key points to consider.
Cost efficiency
One of the primary reasons for outsourcing electronics manufacturing is cost efficiency. By partnering with contract manufacturers or electronic manufacturing services (EMS) providers, companies can leverage economies of scale, reduce capital expenditures, and minimize overhead costs associated with in-house manufacturing facilities.
Outsourcing allows for better control of manufacturing expenses, especially in terms of labor, equipment, and supply chain management.
Acronyms
A lot of acronyms are used in the electronics industry. If you want to know what is the difference between EMS and ODM or OEM and CEM, check out the glossary at the bottom of the page.
Expertise and specialization
Electronics manufacturing requires specialized knowledge and expertise in areas such as PCB assembly, testing, quality control, and compliance with industry standards. Contract manufacturers and EMS providers possess the necessary experience, infrastructure, and skilled workforce to handle complex manufacturing processes efficiently.
Partnering with them allows companies to benefit from their technical know-how and focus on their core competencies.
Flexibility and scalability
Outsourcing electronics manufacturing provides companies with flexibility and scalability in production. Contract manufacturers can quickly adjust production volumes to meet fluctuating market demands. They offer the ability to scale up or down production capacities without significant upfront investments, allowing companies to be more responsive to market dynamics and avoid potential inventory risks.
Access to advanced technologies
Contract manufacturers and EMS providers often invest in state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies and equipment to deliver high-quality products.
By outsourcing, companies gain access to these advanced technologies without the need for substantial investments. This enables them to incorporate the latest innovations, benefit from advanced manufacturing, improve product quality, and stay competitive in the fast-paced electronics industry.
Focus on core competencies
Outsourcing manufacturing activities allows companies to concentrate on their core competencies, such as research and development, marketing, and customer support. By delegating the manufacturing process to external partners, companies can allocate resources effectively, streamline operations, and enhance overall business efficiency.
Global reach and supply chain optimization
Many electronics manufacturing outsourcing providers have a global presence and established supply chain networks. This facilitates access to a broader range of suppliers, reduces lead times, and optimizes the supply chain for improved cost-effectiveness.
Outsourcing can enable companies to tap into international markets, leverage global resources, and expand their reach without establishing physical manufacturing facilities in every location.
It is important for companies to carefully select reliable and reputable contract manufacturers or EMS providers to ensure successful outsourcing partnerships. Effective communication, collaboration, and clearly defined expectations are crucial for achieving desired outcomes and maintaining product quality standards throughout the outsourcing process.
Trends in the consumer electronics industry

The consumer electronics manufacturing industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and products being introduced and old ones becoming obsolete. As such, it can be difficult to keep up with the latest trends in the industry.
However, understanding these trends is important for anyone who wants to stay ahead of the curve. Here are some notable trends shaping the consumer electronics landscape:
- Smart and connected devices — The proliferation of smart and connected devices continues to be a dominant trend. From smartphones and smartwatches to smart home appliances and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, consumers are seeking seamless connectivity and integration across their digital ecosystem.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) integration — AI has emerged as a transformative force in consumer electronics. AI-powered features and voice assistants are becoming more prevalent, enabling personalized user experiences, improved voice recognition, and intelligent automation in devices like virtual assistants, smart speakers, and home automation systems.
- Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) — AR and VR technologies are revolutionizing the consumer electronics industry. Virtual reality headsets, augmented reality apps, and immersive gaming experiences are gaining popularity, while industries like healthcare, education, and entertainment are exploring the potential of AR/VR applications.
- Wearable technology — Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and smart clothing, are witnessing steady growth. Consumers are increasingly adopting wearables to monitor their health and fitness, track daily activities, receive notifications, and access personalized data on the go.
- 5G connectivity — The advent of 5G technology brings faster, more reliable wireless connectivity, opening doors to new possibilities in consumer electronics. 5G enables enhanced mobile experiences, supports real-time streaming, powers IoT devices, and facilitates advancements in areas like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Sustainability and eco-friendly initiatives — Environmental consciousness is influencing consumer electronics trends. More consumers seek eco-friendly and energy-efficient products, prompting manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices, use recyclable materials, and reduce waste.
- Advanced display technologies — Display technologies are evolving to offer improved visual experiences. OLED and QLED displays with vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and slim profiles are increasingly prevalent in smartphones, televisions, and monitors. Foldable displays are also gaining attention, allowing for innovative form factors.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales — The rise of e-commerce has transformed the consumer electronics industry. Consumers now have access to a wide range of products online, and direct-to-consumer sales models are becoming more common, enabling brands to establish a direct relationship with their customers.
It’s worth noting that these trends are dynamic and subject to constant change as technology continues and consumer demands evolve. Manufacturers and industry players need to stay agile and responsive to these trends to remain competitive in the consumer electronics market.
What are the challenges faced in the electronics manufacturing process?
The consumer electronics production industry is one of the most rapidly changing and competitive industries globally. To succeed, companies must constantly innovate and adapt to the ever-changing landscape to stay ahead of the competition.
However, several challenges face the industry. Below we take a look at the 19 biggest challenges of electronic industry.
1. Rapidly changing technology
One of the biggest challenges of the electronic industry is the rapid pace of change. Technology is evolving at an ever-increasing rate. Companies must continually update their products to stay ahead of the competition and avoid aged products becoming dead stock.
This can be a costly and time-consuming process.
2. Short product life cycles
Another challenge faced by the electronics production process is the short product life cycle. Due to the rapid pace of change, products quickly become outdated and must be replaced with newer models. This can result in high levels of waste.
3. Increasing competition
The consumer electronics manufacturing industry is highly competitive. Many companies compete for market share, and new entrants are constantly entering the market. This makes it difficult for companies to differentiate their products and stand out from the crowd.
4. Price pressure
Due to the high level of competition, there is also a lot of pressure on setting selling prices in the consumer electronics industry. Companies are constantly under pressure to reduce prices, impacting margins and profitability.
5. Access to raw materials
Many consumer electronics are made from rare earth metals and other materials that can be difficult to obtain. This can lead to shortages and increased prices. For example, since 2020, there has been a massive global chip shortage which has affected many brands, from Sony to Toyota.
6. Environmental regulations
The electronics manufacturing process is subject to several environmental regulations. These regulations can impact the design, manufacture, and use of products.
7. Changing consumer preferences
Consumer preferences constantly change, making it difficult for companies to keep up with demand. For example, the popularity of smartphones has led to a decline in the demand for traditional phones and other devices.
8. Economic conditions
The consumer electronics manufacturing process is susceptible to economic fluctuations. For example, the global recession in 2008 – 2009 had a significant impact on sales of consumer electronics.
9. Social media pressure
Social media can have a significant impact on the consumer electronics industry. For example, negative reviews or comments about a product can spread quickly and damage a company’s reputation.
10. Intellectual property theft

The consumer electronics industry is also susceptible to intellectual property theft, especially when outsourcing. This can occur when products are copied, or counterfeit products are sold, leading to lost sales and revenue.
11. Supply chain disruptions
The electronics manufacturing process is reliant on a complex global supply chain. This can make it vulnerable to disruptions, such as natural disasters or political instability. All of which will greatly affect your manufacturing lead time.
12. Data security risks
As more and more products become connected, data security risks are increasing. Hackers could gain access to personal data or company secrets, leading to serious consequences.
13. Labour issues
The consumer electronics industry is often criticized for its labor practices. For example, there have been allegations of poor working conditions and low factory wages in developing countries.
14. Emerging markets
The consumer electronics industry is increasingly focused on emerging markets. However, these markets can be challenging due to their different cultures, languages, and business practices.
15. Sustainability
The electronics manufacturing process is under pressure to become more sustainable. For example, there is a growing demand for products made from recycled materials.
16. End-of-life management
When products reach the end of their life, they must be disposed of properly to avoid environmental pollution. This can be a challenge for the consumer electronics industry due to the many discarded products each year.
17. Warranty and support
Customers often expect a high level of warranty and support for their products. This can be costly for electronics companies, especially if faulty products break down soon after purchase.
18. Counterfeit products
The sale of counterfeit products is a major problem in the consumer electronics industry. This can damage a company’s reputation and lead to lost sales.
19. Product recalls
Product recalls can be costly and damaging to a company’s reputation. They can also lead to legal problems if customers are injured, or products are found to be defective. This is why it’s important to have traceability software implemented now to be ready for such a scenario.
Katana for the electronics manufacturing industry
Katana is the ultimate cloud manufacturing platform for managing everything from sales, to production and inventory management. Read all about Katana electronic manufacturing software here.
Streamline your electronics manufacturing process with Katana
Having electronics manufacturing software to monitor activity is essential because, at the drop of a hat, anything could happen that delays production and leaves customers disappointed.
Introducing Katana, the ultimate platform for those working in the electronics production industry.
Katana offers real-time insights into sales, operational status, and costing, allowing business owners to make better decisions on the fly. Katana comes with essential features for electronics manufacturers to help them manage their entire business from a centralized platform.
Inventory management
Easily track your raw materials, WIP, and finished goods inventory in real time. Katana updates your stock levels whenever new orders come in, so you always know exactly what you have in stock.
With its real-time master planner, you can quickly reprioritize your orders, and Katana automatically allocates the necessary resources to get the most important orders out the door first.
Katana also supports multilocation inventory and multichannel sales, letting you manage your stock and sales globally.
End-to-end product traceability
Quality assurance is of the utmost importance when manufacturing electronic goods.
Proper end-to-end product traceability thanks to serial number tracking allows manufacturers to quickly:
- Organize a product recall
- Launch an investigation
- Respond to a warranty claims
This feature will allow you to get complete visibility of your item’s journey to uncover which batch a product came from, the raw materials used, or which supplier sold you the components used.
COGs and manufacturing costs
Katana accurately tracks production costs based on the price of ingredients and the cost of your electronics manufacturing process.
This allows you to track the profitability of your sales. Over at the sales screen, you can see the cost of goods sold and profit for all your sales orders. These cost calculations are performed automatically, so you don’t have to worry.
Contract manufacturing
Katana supports contract manufacturing, automating your production tracking and monitoring with your contractor.
With Katana, you can have raw materials sent directly to your CM while monitoring inventory levels and the status of tasks from their end. If you use a CM for building sub-assemblies, no problem. With Katana, you can issue them a manufacturing order instead and keep an eye on production via the software.
See how Katana can benefit your electronics manufacturing process. Get started by booking a demo
with Katana, and take your contract manufacturing business to the next level.
Electronics manufacturing glossary
- Original equipment manufacturer (OEM) — An OEM is a company that designs and manufactures products based on specifications provided by another company. The products are then sold under the brand name or label of the company that commissioned their production.
- Electronic manufacturing services (EMS) — EMS refers to companies that offer a range of manufacturing services for electronic products. These services can include design, assembly, testing, supply chain management, and sometimes even after-sales support for the products.
- Contract electronics manufacturer (CEM) — A CEM is similar to an EMS provider and refers to companies that contractually manufacture electronic products on behalf of other companies. CEMs typically offer a comprehensive range of services, including design, prototyping, production, and logistics.
- Original design manufacturer (ODM) — An ODM is a company that designs and manufactures products based on its own specifications and expertise. ODMs often offer ready-made products or solutions that can be customized or rebranded by other companies to suit their requirements.
- Contract manufacturing organization (CMO) — A CMO is an organization that specializes in manufacturing products on a contract basis for other companies. While the term is not specific to the electronics industry, it can be used to refer to companies that provide manufacturing services for electronic products.
Sources
¹Demographics of Mobile Device Ownership and Adoption in the United States, Pew Research Center (2021)
²Unpacking the Boom in U.S. Construction of Manufacturing Facilities, US Department of the Treasury (2023)

James Humphreys
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control