What is PPE manufacturing, and why is it important?
Everything you need to know about PPE manufacturing equipment and how to use them within your own production lines.

James Humphreys
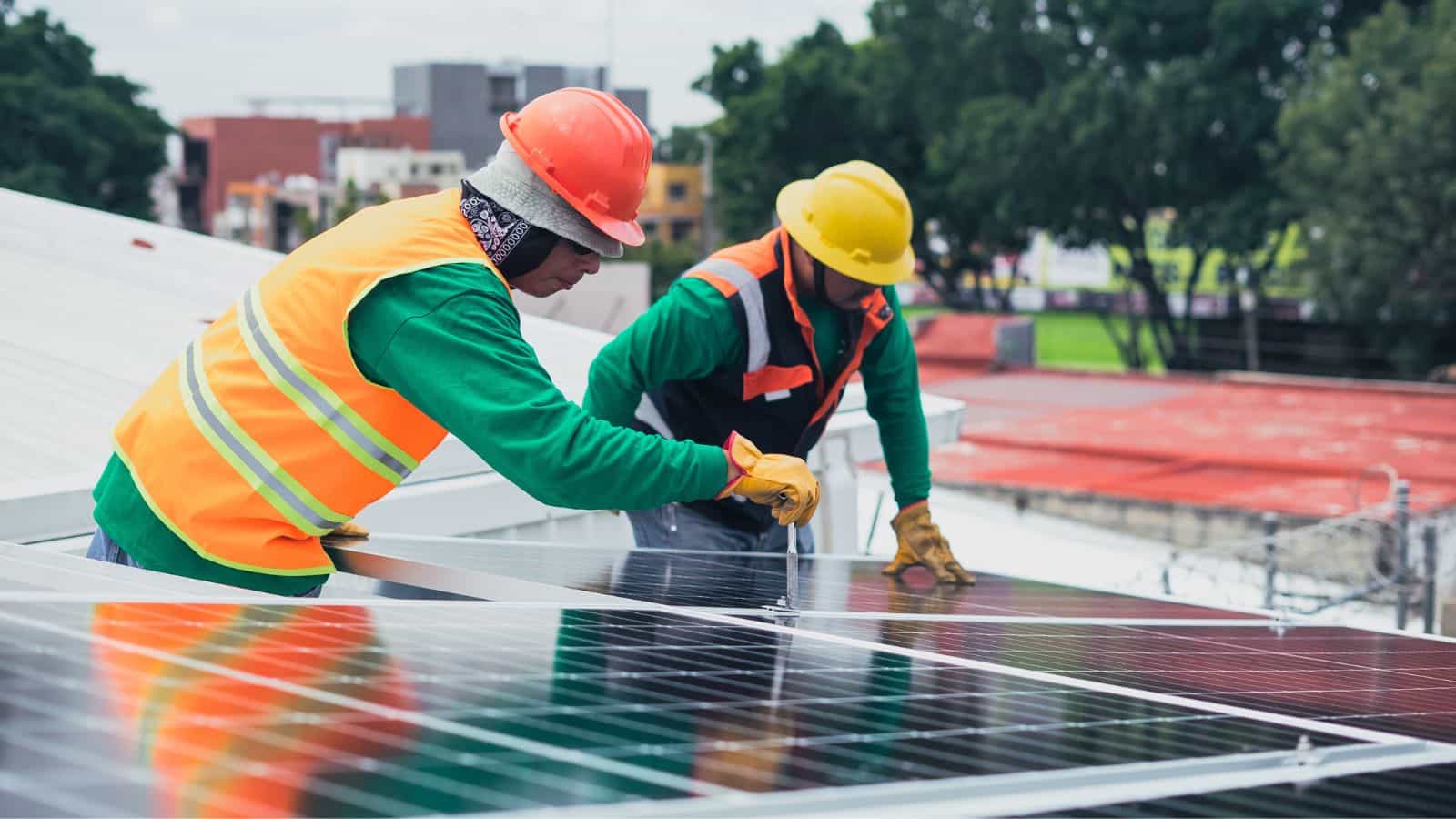

With the pandemic, we have long heard about the importance of PPE from various health organizations and governments. While it is still a good habit to use PPE in our daily lives, it is just as important to understand it in the context of manufacturing.
In manufacturing industries, PPE is associated with workplace hazards. These can appear in many different forms: falling debris, sharp materials, chemicals, and noise, among other potentially dangerous situations. It is important to protect employees from workplace hazards that can cause injury.
The following post will cover four topics:
- What is PPE in manufacturing?
- Why PPE is important in manufacturing
- Examples of PPE equipment for manufacturing
- Steps to administer manufacturing PPE
Are you ready to gain a comprehensive understanding of PPE manufacturing? Let’s begin.
What does PPE stand for in manufacturing?
PPE stands for personal protective equipment. This gear protects workers from potential hazards while on the job. Common items considered PPE include gloves, safety glasses, and earplugs. Employers must provide their employees with the proper PPE for the specific task. Failure to do so can result in serious injuries or even death.
What is PPE in manufacturing?
Personal protective equipment, commonly referred to as PPE, is equipment worn to avoid various hazards in manufacturing facilities. Gloves, protective hearing gear (earplugs, muffs), hard hats, goggles, respirators, and full-body suits are just a few examples of PPE.
PPE ensures more safety and reassurance in a dangerous manufacturing environment. It can be the difference between a minor injury and a life-threatening one.
While many argue that PPE can interfere with work or be uncomfortable, the benefits of wearing it far outweigh the drawbacks. Most companies have policies in place that require employees to wear certain types of PPE while on the job.
There are many personal protective equipment types, each with a specific purpose. The type of PPE manufacturing you need will depend on the hazards present in your workplace. For example, if you work with chemicals, you may need different equipment than someone who works with heavy machinery.
No matter what type of manufacturing job you have, there is some form of personal protective equipment that can help keep you safe. Do your research and make sure you are using the correct PPE for your specific job. Your life may depend on it.
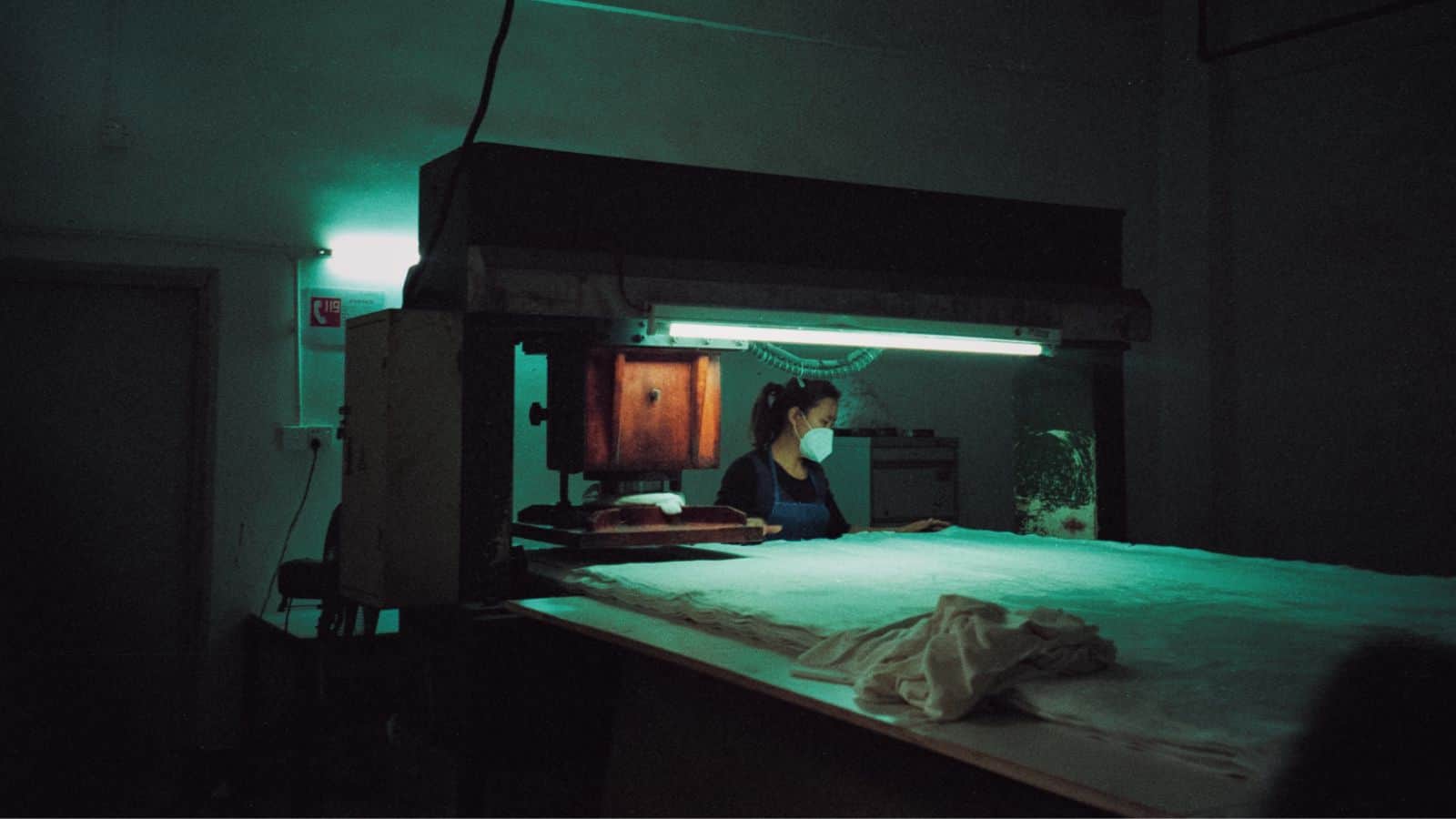

Why is PPE important in manufacturing?
PPE manufacturing is important for the following five reasons:
- Protection — PPE protects workers from injuries caused by exposure to hazardous materials, including chemicals, noise, heat, and flying debris. It can also help prevent or reduce the severity of injuries that do occur. Workers are the backbone of any operation, and their safety should be a priority
- Productivity — Wearing PPE can help workers feel more comfortable while performing their tasks, which can lead to increased productivity
- Morale — A safe workplace is also a happy workplace. When workers feel confident that they are protected from potential injuries, they are more likely to have a positive attitude and be motivated to do their best work
- Compliance — In some cases, wearing PPE may be required by law or regulation. For instance, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) has noise exposure limits that require workers to wear hearing protection when working in loud environments
- Cost savings — Injuries can be costly, both in terms of medical expenses and lost productivity. By preventing injuries, PPE can help save money for employers and workers alike. Expenses related to workplace injuries and illnesses are estimated to cost more than $170 billion annually
Examples of PPE for manufacturing
You will have to use different types of PPE depending on the manufacturing hazards to which your workplace is subject.
Here are 10 PPE manufacturing use cases:
- Breathing masks — These can prevent you from breathing in toxic chemicals. Depending on the facility, you may need a simple paper mask or a more complex respirator. Wearing a mask at work will also prevent long-term respiratory problems
- Protective clothing — Many manufacturing facilities require workers to wear protective clothing. This could include items such as gloves, aprons, overalls, and boots. The type of clothing you need will depend on the nature of the work you are doing
- Earplugs or earmuffs — Manufacturing facilities can be noisy, so it is important to protect your hearing. Earplugs or earmuffs will help to reduce the noise levels that you are exposed to
- Safety glasses — Often there is a risk of flying debris or chemicals getting into your eyes. Wearing safety glasses will help to protect your eyes from these hazards
- Face shields — Face shields provide additional protection for your face, eyes, and mouth. They are often used in conjunction with safety glasses or goggles when manufacturing facilities are especially dangerous
- Hard hats — Essential in some manufacturing environments where there is a risk of objects falling from above. They protect your head from impact and help to prevent serious injuries
- Life jackets — There are times when workers should wear life jackets. This is usually the case when working near water. Lifejackets are buoyant and could help save you from drowning
- Fall protection — When working at heights, there is a risk of falling. Wearing fall protection, such as a harness, will help to prevent serious injuries if you do fall
- Fire extinguishers — Fire extinguishers are essential in any workplace, but they are especially important in manufacturing facilities. Having a fire extinguisher close at hand can help to prevent serious injuries or damage to property
- First aid kit — A first aid kit should be available in all workplaces, including manufacturing facilities. This is because accidents can happen at any time, and it is important to be prepared for them. First aid kits should include bandages, disinfectant, and pain relief medication
There are many other examples, such as welding helmets, fire-retardent leggings, or fully-sealed body suits. The key to PPE manufacturing safety is wearing the right equipment for the job you are doing and ensuring that it is properly fitted to protect you effectively.
Steps to administering manufacturing PPE properly in the workplace
Administering manufacturing PPE in the workplace is no easy task. It takes great coordination and communication to ensure that everyone is on the same page and knows what is expected of them.
1. Hazard assessment
A hazard assessment allows you to identify physical and health hazards in the workplace. It begins with a walkthrough survey of the facility to develop a list of potential hazards in the following basic hazard categories:
- Impact
- Penetration
- Compression (roll-over)
- Chemical heat/cold
- Harmful dust
- Light (optical) radiation
- Biologic
In addition to noting the basic layout of the facility and reviewing any history of occupational illnesses or injuries, eight things to look for during the walkthrough survey include:
- Sources of electricity
- Sources of motion, such as machines or processes where movement may result in an impact between personnel and equipment
- Sources of high temperatures that could result in burns, eye injuries, or fire
- Sources of harmful dust
- Sources of light radiation, such as welding, brazing, cutting, furnaces, heat treating, high-intensity lights, etc
- The potential for falling or dropping objects
- Sharp objects that could poke, cut, stab or puncture
- Biologic hazards such as blood or other potentially infected material
2. PPE manufacturing selection and inspection
Select which PPE will be used to combat each hazard in your assessment. Make sure to sign and date your selection form.
Once selected, make sure that all PPE is in good condition and has no damage that could potentially harm the wearer. If there are any concerns, do not hesitate to replace the item or repair it if possible.
3. Training
After the assessment and selection, employees required to use PPE must be trained before they use it. Critically, everyone must understand the plan, so there is no confusion later on. Re-training should be done if PPE manufacturing requirements change and as needed.
The following must be covered:
- What PPE to use and when to use it
- Limitations of the PPE
- How to put it on, take it off and adjust it
- Inspection and maintenance
- Any manufacturer instructions and warnings
- Make sure the PPE fits well
- How to obtain PPE
- How to dispose of PPE
- How to use lot tracking software for finding contaminated items
4. Documentation
Remember to document the following information from your PPE hazard assessment, PPE selection, and training just in case you need to look back on it in the future. This will ensure that you have a record of what was done in case there are any questions or problems later on.
- Specific job, process, or activity being assessed
- Hazards identified
- Selection of PPE used for each hazard identified. Specify the PPE type, brand, model
- Employees identified to use PPE
- Name and title of the person completing the hazard assessment
- Date hazard assessment was completed
- Name, title, and training date for all employees required to wear PPE
Extend the protection to customers
Keep track of products by assigning lot numbers to manufacturing and sales orders to monitor expiring stock, and never lose track with batch identification with Katana.
Keeping everyone safe and happy
There you have it. Now you know what PPE is in manufacturing, why it is important, and the steps to administer manufacturing PPE properly in the workplace.
Protecting workers with PPE should always be a priority for any manufawwcturing employer, and it starts with managing your PPE inventory.
Katana’s end-to-end cloud inventory platform can help you keep track of your inventory movements, from purchasing them as supplies and shipping them out as a final product. Easily set reorder points so that you can avoid PPE-related shutdowns.
Book a demo and see for yourself how Katana can streamline your operations.

James Humphreys
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control