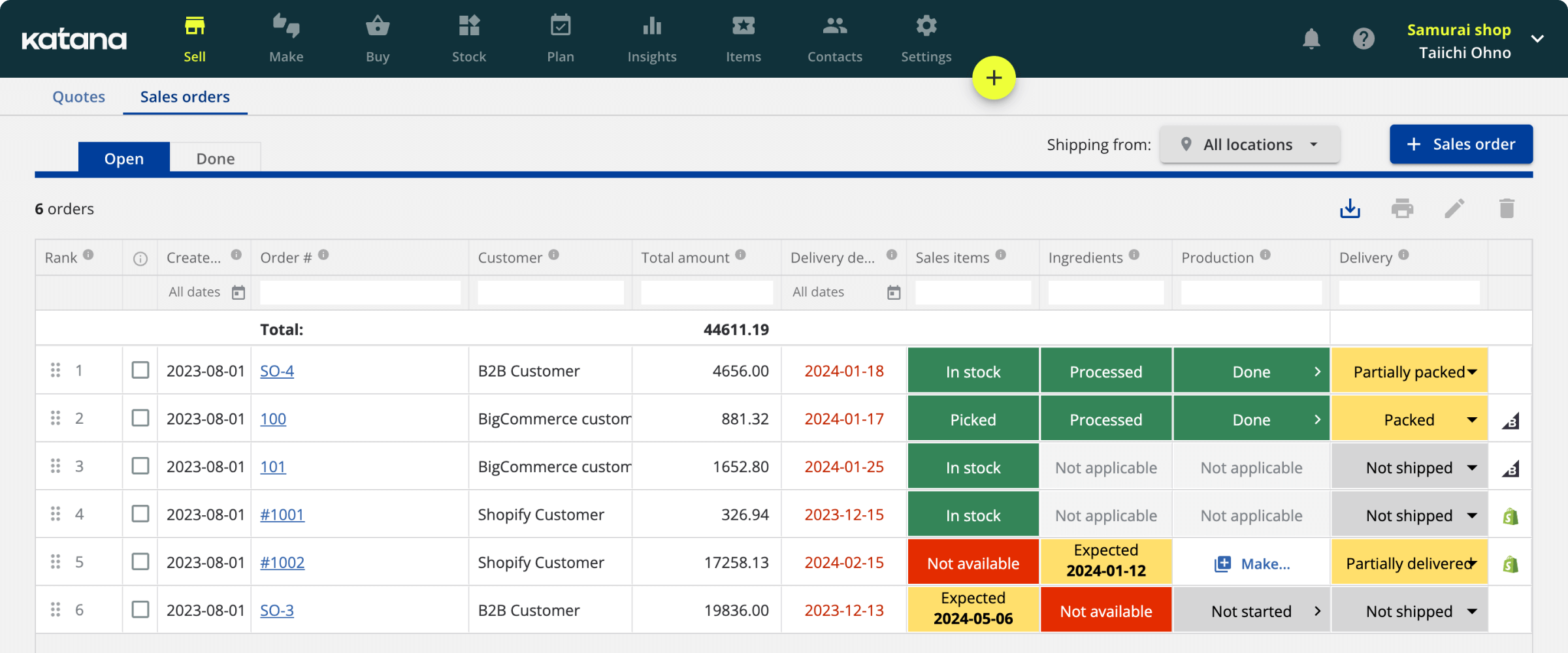
Centralized vs. decentralized manufacturing
Choosing between centralized or decentralized manufacturing is a critical decision that can affect your company in the long run. In this article, we explore the differences between the two approaches and guide you in deciding which one is a better fit for your business.

Henry Kivimaa

With the recent developments around the world, including a certain virus that shall remain nameless for now, remote work has been increasingly popular.
People have moved to hybrid work, some even working remotely 100% of the time. Home offices are definitely a thing now, especially since more and more tasks are automated and digitalized. Amid all this, a question arises:
Why do businesses need to operate in one place anymore?
For the longest time, manufacturers have been huddled up in huge factories, some the size of an average university campus.
This is the way it has always been and it has proved to be a success. However, a new kid on the block is causing a stir in the manufacturing world — decentralization. So which approach is better and guarantees a bigger payoff?
Let’s compare them side by side, pageant style, and put the conversation finally to bed.
What is centralized manufacturing?
Centralized manufacturing is a production model where all manufacturing processes occur in a single location, often owned and operated by one company.
This manufacturing approach allows better quality control and oversight of the entire production process, as well as adapting to changing market demands.
Centralization in manufacturing is characterized by economies of scale, where mass production leads to lower unit costs. It is commonly used to produce goods that require a complicated and expensive production process.
In centralized production, the company controls all aspects of manufacturing, from sourcing raw materials to shipping finished products.
Advantages of centralized manufacturing
Centralized manufacturing has several advantages, such as:
- Economies of scale — With all processes happening in one place, production tends to run faster and more efficiently, resulting in lower costs per unit.
- Standardization — By gathering all teams under one roof, their work processes follow similar standards and quality control processes, making it easier to maintain consistency in product quality.
- Efficient resource utilization — Resources such as equipment, labor, and materials can be used more efficiently across teams.
- Simplified supply chain management— The manufacturing supply chain management is simplified as all production processes occur at a single location, reducing the complexity of logistics and inventory across multiple locations.
- Specialization — Centralized production facilities tend to specialize in specific products or processes, leading to greater expertise and efficiency.
- Lower administrative costs — A centralized manufacturing system means lower administrative costs, as there is only one location to manage.
Disadvantages of centralized manufacturing
Centralized manufacturing can have some disadvantages, like:
- Greater vulnerability to disruptions — If there is a disruption in the facility, it can impact the entire production process, leading to delays and downtime in production.
- Higher transportation costs — If manufacturing is done in a single location, products must be transported to their final destination, leading to higher shipping costs and longer lead times.
- Lack of responsiveness — A centralized factory may not be able to respond to changing customer needs or market trends quickly enough. This can mean missing opportunities or losing market share.
- Limited customization — As it may not have the flexibility to adapt to individual customer needs, centralized manufacturing may be less able to offer customized products or services.
- Higher inventory costs — Centralized production often requires holding large amounts of inventory to ensure a steady supply of products. This can lead to higher stock-carrying costs and the risk of overstocking or dead stock.
Get a free batch production ebook
Download the free ebook to learn everything you need to know about batch production — from what it is to industry use cases to software that will help you implement batch production workflows.
What is decentralized manufacturing?
Decentralized manufacturing is a production model where production occurs in multiple locations, meaning that manufacturing is distributed between separate facilities.
This model allows more customization to meet the needs of specific regions, reducing transportation costs and providing local job opportunities.
Decentralized production can be owned and operated by multiple companies, including suppliers, contract manufacturers, and third-party logistics providers. In this model, companies can focus on their primary areas of expertise and outsource other production processes to competent partners.
Advantages of decentralized manufacturing
Decentralized manufacturing can offer several advantages, including:
- Greater flexibility and responsiveness — Decentralized production can respond more quickly to changing customer needs and market trends, as production can be adjusted at each location depending on the necessary steps.
- Lower transportation costs — Products can be produced and distributed locally, reducing transportation costs and lead times.
- Reduced vulnerability to disruptions — Spreading production across multiple locations means that issues at one facility can be contained, minimizing the risk of supply chain interruptions.
- Customization — Decentralized manufacturing can offer more customization options, as each location can more easily adapt to meet local customer needs and preferences.
- Reduced inventory costs — Decentralized production often requires less inventory than centralized manufacturing, as production can be more closely matched to local demand.
- Supporting local economy — Running production and operations across multiple locations creates more jobs in local communities, helping to support economic development and bringing jobs closer to people.
Disadvantages of decentralized manufacturing
Decentralized manufacturing can also have some disadvantages, such as:
- Increased administrative costs — Decentralized production requires duplication of many resources, like labor, equipment, and facilities, to manage production across multiple locations.
- Greater difficulty in standardizing product quality — Since production processes are spread across multiple locations, ensuring consistent product quality across all areas can be more difficult.
- Higher capital investment — Decentralized manufacturing usually requires a higher capital investment to provide equipment and create infrastructure at each location.
- Coordination challenges — Managing production processes across multiple locations can be more challenging, requiring greater coordination and communication across teams to ensure smooth operations.
- Reduced economies of scale — Decentralized production tends to have higher manufacturing costs per unit since production is scattered around different locations, thus not benefiting from the economies of scale as centralized manufacturing does.
What are the main differences between centralized and decentralized manufacturing?

With both still focusing on manufacturing and putting out the best product, there are many core differences that distinguish centralized and decentralized manufacturing from each other. The main differences between centralized and decentralized manufacturing are as follows:
Location
In centralized manufacturing, all production processes occur in a single location, and all teams operate under one roof. Decentralized manufacturing is a multilocation business, with each step of production potentially happening in a different facility.
Ownership
Centralized manufacturing is often owned and operated by a single company. Decentralized manufacturing can be owned by multiple companies, meaning that different business entities are responsible for their own operations and production processes.
Scale
Centralized manufacturing largely benefits from economies of scale, bringing the cost per unit down but also meaning less flexibility towards customizations. Decentralized manufacturing can be more flexible and adaptable to local market needs but typically has a higher cost per unit.
Supply chain management
In centralized manufacturing, the owning business is responsible for all materials, equipment, and operations. Decentralized manufacturing means that all owning companies need to ensure a steady supply flow for their processes, being indirectly responsible for the smooth flow of other related functions and companies too.
How can Katana help with centralized vs. decentralized manufacturing?

Katana is a cloud manufacturing software that can help you tie all your business operations together onto one platform. It has many beneficial features, including the following.
Inventory management
Whether you operate from one central facility or multiple locations, Katana can help you manage inventory in all warehouses. The system offers a live overview of your stock and automatically adjusts the numbers based on sales and manufacturing updates. You can also keep an eye on supplies and raw materials, helping you make better business decisions and prioritize production based on availability and customer demand.
Production scheduling
Regardless of your manufacturing approach, production planning and scheduling are still necessary, and Katana makes it easier than ever. Create tasks and assign them to your operators to complete using the Shop Floor App. Gain total shop floor control and keep up with deadlines in your centralized location and across all operations.
Pro tip: If you’re not ready to commit to software yet or are looking for a more hands-on production scheduling solution, try a free downloadable production schedule template.
Integrations
Katana offers many integrations to enhance your manufacturing management experience. Or, if you’ve already found software you would like to keep using, build it into your workspace and create a custom flow for your business using Katana’s open API.
Insights
Track and analyze data based on sales, production, customers, and orders. Katana creates valuable insights and helps you make better business decisions. Manufacturing analytics can be used for demand planning, better inventory management, and production scheduling.
Ultimately, comparing centralized and decentralized manufacturing is like comparing apples and oranges. One is suitable for apple pie, the other for a glass of OJ, but they can never substitute for each other. It all boils down to personal preference.
Centralize your business operations with Katana
Book a demo to get all your questions answered regarding Katana’s features, integrations, pricing, and more.

Henry Kivimaa
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control