Batch scheduling for improved production optimization
Unlocking the potential for streamlined production and resource optimization. Learn how batch schedule empowers manufacturers to boost efficiency and meet production goals effectively.

Henry Kivimaa

The term batch scheduling has its roots in the early days of computer systems and data processing. It emerged when computers were primarily used for large-scale data processing tasks. During that time, computer operations were typically performed in batches, where a group of similar or related jobs were collected together and executed sequentially.
As the practice of organizing and planning these batches became more refined, the term batch scheduling came into use to describe the process of arranging and sequencing jobs within these batches. It became an integral part of managing computer operations and maximizing the efficiency of data processing systems.
Over time, the concept of batch scheduling expanded beyond computer systems and found applications in various industries, including manufacturing.
This post explores manufacturing batch scheduling, how it works, what the benefits are, and the best way to manage it.
What is batch scheduling?
Batch scheduling or bulk scheduling in manufacturing refers to the process of planning and organizing production activities to optimize the use of resources and increase efficiency. It involves grouping similar or related tasks or orders together into batches and then scheduling those batches for production.
This approach allows for the efficient utilization of equipment, materials, and labor by reducing setup times and maximizing productivity.
Batch scheduling aims to minimize downtime, improve workflow, and reduce costs by streamlining the production process and sequencing tasks in a logical and efficient manner.
How does batch scheduling work?
Batch scheduling is a whole process that usually consists of the following steps:
- Job analysis
- Batch formation
- Resource allocation
- Sequencing
- Scheduling
- Execution and monitoring
- Feedback and continuous improvement
Let’s review these in more detail.
1. Job analysis
In the job analysis phase, manufacturing managers or planners carefully analyze and evaluate the production tasks or jobs that must be scheduled. They consider factors such as task requirements, dependencies, priorities, and any constraints associated with the jobs.
This analysis helps identify similarities or relationships between different tasks, determining the formation of batches.
2. Batch formation
Based on the analysis of jobs, the next step is to form batches. This involves grouping together similar or related jobs to create batches.
The criteria for batch formation can vary depending on the specific industry and production requirements. Typical criteria include product similarity, equipment requirements, order quantities, or production deadlines.
By forming batches, manufacturing companies can minimize setup times and improve overall efficiency.
3. Resource allocation
Once the batches are formed, the next crucial step is resource allocation.
Manufacturing planners need to determine the availability and allocation of resources required for each batch. This includes considering machines, equipment, labor, materials, and any other necessary resources.
Efficient allocation ensures that the required resources are available at the right time and in the appropriate quantities, enabling smooth and uninterrupted production.
4. Sequencing
Within each batch, the sequencing of jobs is determined. Sequencing refers to the order in which the jobs will be executed within a batch. Several factors influence sequencing decisions, such as job priorities, setup times, resource availability, and constraints.
Employees strategically arrange the sequence of tasks to minimize idle time, reduce changeovers, and optimize the utilization of resources. This step ensures that jobs within a batch are executed in the most efficient and logical manner.
5. Scheduling
After determining the sequencing of jobs within batches, the next step is to schedule them for production.
Scheduling involves assigning specific time slots or periods for each batch to be processed based on the overall production schedule, resource availability, and production capacity.
Manufacturing planners need to consider machine availability, labor shifts, and any specific production requirements or constraints. An effective scheduling process ensures that the right batches are scheduled at the right time to meet production targets and customer demands.
6. Execution and monitoring
Once the batches are scheduled, they are executed according to the established plan. During this phase, close monitoring of batch progress is essential. Workers track the actual performance of each batch, compare it with the scheduled plan, and identify any deviations or bottlenecks.
Monitoring helps detect issues, such as delays, resource shortages, or quality concerns and enables timely interventions to maintain productivity and efficiency.
7. Feedback and continuous improvement
The completion of each batch provides an opportunity for feedback and continuous improvement.
Manufacturing companies collect feedback on various aspects, such as production time, quality, resource utilization, and any challenges encountered. This feedback is analyzed and evaluated to identify areas for improvement in the batch scheduling process.
Continuous improvement efforts aim to streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and enhance overall productivity in subsequent scheduling iterations.
Example of batch scheduling

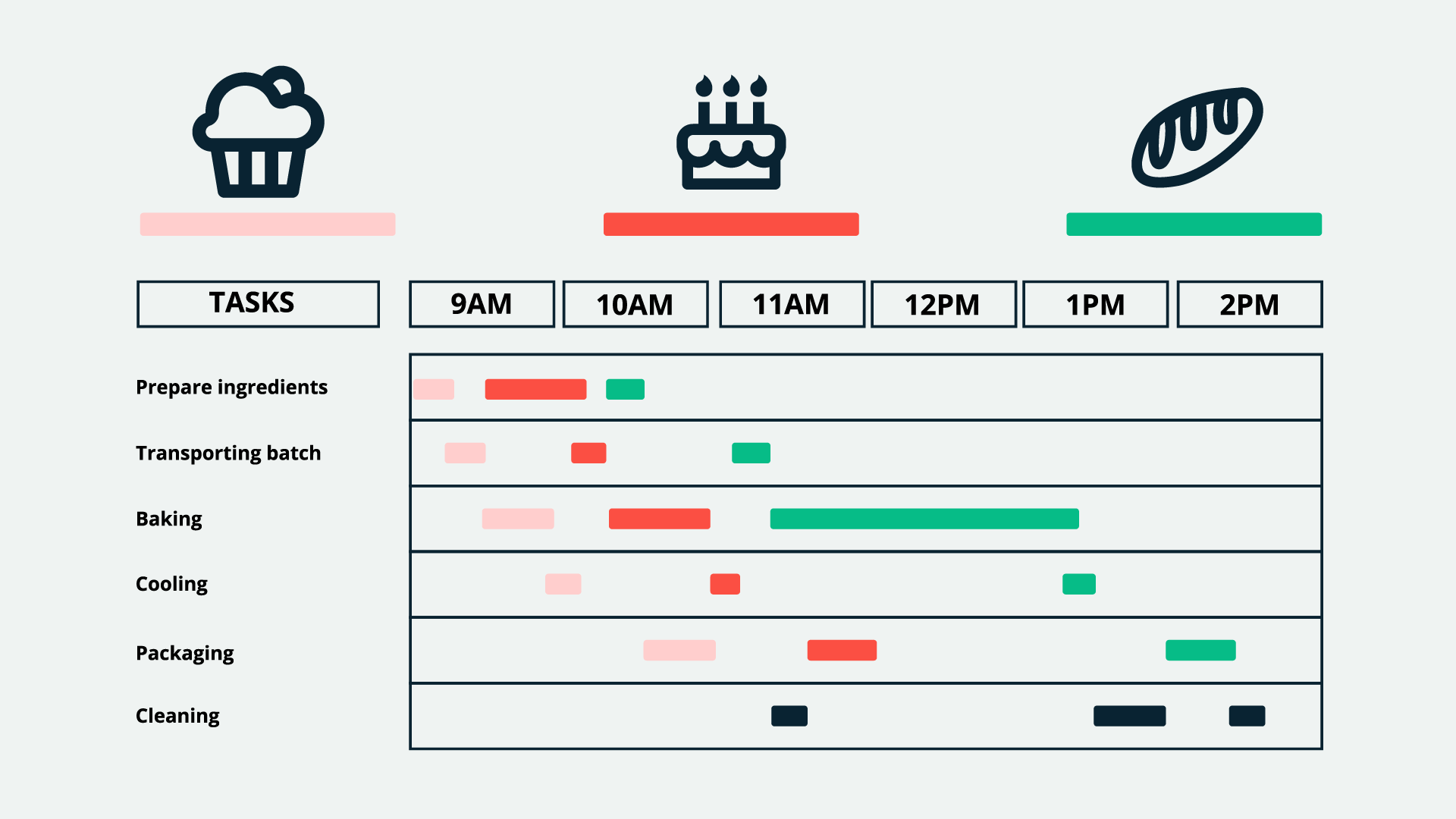
Let’s consider an example of batch scheduling in a food manufacturing company that produces various baked goods such as cookies, muffins, and bread. Here’s how bulk scheduling can be applied in this scenario:
- Job analysis — The manufacturing team analyzes the different baking tasks required for each product. They consider baking time, temperature, ingredients, and equipment requirements. They identify similarities and differences between the tasks, such as shared oven usage, common ingredients, or similar baking temperatures.
- Batch formation — Based on the job analysis, the team groups similar baking tasks together to form batches. For instance, they may create a batch for cookies that require a similar temperature and can be baked together in the same oven. Another batch may include muffins that have similar baking times and ingredient requirements. By forming batches, the company can minimize oven setup time and optimize the utilization of available resources.
- Resource allocation — The team determines the resources needed for each batch, including oven availability, mixing equipment, baking trays, and labor requirements. They ensure that the necessary resources are appropriately allocated to each batch, considering factors such as equipment capacity, maintenance schedules, and staff availability.
- Sequencing — Within each batch, the team establishes the sequencing of tasks. They look at product demand, production deadlines, and customer orders. For example, they may prioritize baking that batch earlier if there is a rush order for cookies. The sequencing is also influenced by cooling and packaging times to ensure efficient post-baking processes.
- Scheduling — Once the sequencing is determined, the batches are scheduled for production. The workers assign specific time slots or periods for each batch based on the overall production schedule and resource availability. They take into account oven availability, staff shifts, and any specific customer delivery requirements. The schedule ensures that batches are produced on time to meet customer demands while optimizing resource utilization.
- Execution and monitoring — The scheduled batches are then executed according to the established plan. The team closely monitors the progress of each batch, tracking baking times, quality parameters according to their production quality control checklist, and adherence to the schedule. Any deviations or issues are promptly addressed to ensure a consistently high quality products get handed over to the food distributor.
- Feedback and continuous improvement — After completing each batch, the team collects feedback on various aspects, such as baking time, product quality, and resource utilization. They analyze this feedback to identify areas for improvement. For example, they may identify opportunities to reduce baking time or adjust ingredient quantities for better efficiency and quality. Continuous improvement efforts help refine the batch scheduling process over time.
Now that it’s clear how batch scheduling works let’s review the benefits of this strategy.
Katana’s cloud inventory software for simplified batch management
Katana equips you with everything you need to take control of your batches, including production scheduling, inventory management, batch and expiry date tracking, and much more.
What are the benefits of batch scheduling?
Batch scheduling offers several benefits that contribute to improved operational efficiency and productivity. Here are some key advantages:
- Resource utilization — Batch scheduling allows for optimal utilization of resources such as machines, equipment, labor, and materials. Grouping similar tasks reduces setup times and minimizes the need for frequent equipment changeovers. This leads to improved efficiency and increased output per unit of time.
- Reduced downtime — Bulk scheduling minimizes the transition time between tasks. Consecutively executing similar jobs reduces production downtime associated with setup, preparation, and clean-up, resulting in higher production uptime and overall equipment effectiveness.
- Streamlined workflow — Batching similar tasks enhances the flow of work on the shop floor. It simplifies the production process by reducing variations and complexities associated with frequent job changes. This enables smoother operations, reduces disruptions, and improves overall workflow efficiency.
- Enhanced productivity — Batch scheduling optimizes the sequencing and arrangement of tasks, leading to improved productivity. Minimizing idle time and maximizing the utilization of resources, production throughput is increased, allowing companies to produce more output within a given timeframe and meet customer demands effectively.
- Improved planning and control — Bulk scheduling provides a structured approach to planning and controlling production activities. It enables manufacturers to create a well-defined schedule, allocate resources efficiently, and have better visibility into production timelines. This leads to improved decision-making, reduced lead times, and increased responsiveness to changes in customer demands.
- Cost savings — Efficient resource utilization, reduced downtime, and improved productivity all contribute to cost savings. Batch scheduling helps minimize waste, optimize inventory levels, and reduce overall operational costs. By maximizing available resources, companies can achieve higher production volumes at lower costs per unit.
- Flexibility and adaptability — Batch scheduling allows for flexibility in adjusting production schedules based on changing priorities, demand fluctuations, or unforeseen circumstances. It provides a framework for incorporating new orders or accommodating rush jobs without disrupting the entire production process.
Implementing effective batch scheduling strategies helps companies achieve higher efficiency, competitiveness, and customer satisfaction.
Batch scheduling software
Katana is a highly regarded cloud-bassed inventory management software for small and medium-sized manufacturers. It provides an array of robust features, including:
- Intuitive production scheduling — A user-friendly interface to easily track production timelines, assign tasks, and set priorities
- Batch tracking — Easily track each batch’s status, identify potential delays and quality issues, and maintain control over the production workflow.
- Inventory management — Real-time visibility into inventory levels, materials, and components enables manufacturers to maintain optimal stock levels for each batch. Automated stock adjustments, reorder point alerts, and inventory optimization features contribute to preventing stockouts and minimizing carrying costs.
- Resource planning and allocation — Allocate resources such as machines, equipment, and labor to specific orders.
- Real-time data and analytics — Katana’s Insights dashboards display key production metrics, including production times, material consumption, and productivity. This data-driven approach enables manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, monitor KPIs, and make informed decisions for process improvements.
- Integrations — Seamless connectivity with various business systems, such as e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce) and accounting software (QuickBooks Online, Xero). This eliminates manual data entry and ensures accurate and up-to-date information across different departments.
Get started by booking a demo with Katana, and take your batch scheduling to the next level.
Batch scheduling FAQs
A batch processing system is a computerized method of executing a series of related tasks or jobs as a group, known as a batch, without requiring immediate user interaction. In a batch processing system, multiple tasks with similar characteristics are grouped together and processed sequentially without interruption. This approach allows for efficient utilization of computing resources by minimizing setup and overhead times.
Batch processing systems are commonly used in various domains, including data processing, banking, manufacturing, and administrative tasks. In such systems, batches are typically processed in a specific order based on predefined rules or priorities. The system reads input data for each batch, performs the required processing or calculations, and generates the desired output or results.
Batch processing systems offer advantages such as automation, scalability, and the ability to process large volumes of data efficiently. They are particularly suitable for handling repetitive, time-consuming, or computationally intensive tasks. Examples of batch processing systems include payroll processing, report generation, data backups, and end-of-day financial processing.
Job scheduling and batch processing are two distinct approaches to managing production tasks:
- Job scheduling — The process of scheduling individual tasks or jobs within a manufacturing environment. Each job is treated as a separate entity and scheduled based on specific requirements, priorities, and deadlines. Job scheduling focuses on optimizing the flow of individual tasks, often considering factors such as machine availability, labor requirements, and production timelines for each job. It involves scheduling tasks individually and monitoring their progress throughout the production process. Job scheduling is commonly used in industries where customization or high variability of products is involved, such as custom manufacturing or job shops.
- Batch processing — The execution of a series of similar or related production tasks as a collective unit. Instead of treating each task individually, batch processing aims to maximize efficiency by reducing setup times and optimizing resource utilization. Batches are formed based on product similarity, equipment requirements, order quantities, or production deadlines. The tasks within a batch are then executed sequentially, often without immediate user interaction, to minimize downtime and improve overall productivity. Batch processing is commonly used in industries requiring high-volume production of standardized products, such as food manufacturing or automotive assembly lines.
To summarize, job scheduling focuses on optimizing individual tasks or jobs within a manufacturing environment, while batch processing involves grouping similar tasks to maximize efficiency and productivity. Job scheduling is suitable for industries with customization and high variability, while batch processing is more suitable for industries with standardized production processes and high-volume output.
A batch scheduler acts as a powerful tool for coordinating and optimizing the scheduling of production batches. It enables users to analyze production requirements, plan and sequence batches, allocate resources, and monitor batch progress.
The software ensures that batches are scheduled efficiently, maximizing resource utilization, minimizing downtime, and meeting production targets.
It facilitates the resolution of any issues or deviations, allows for adjustments to the schedule, and provides valuable performance insights for continuous process improvement. In essence, batch scheduling software streamlines operations, enhances productivity, and ensures a smooth production flow.

Henry Kivimaa
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty with Katana Cloud Inventory — AI-powered for total inventory control