Supply chain disruption examples from 2018 to 2022
In this article, you can find eight real-life supply chain disruption examples from 2018 to 2022 that affected global trade.

James Humphreys

The past four years have given us plenty of supply chain disruption examples to study.
And while governments and businesses enact policies and employ strategies to try and mitigate the economic devastation that major supply chain disruptions can cause — disruptions will likely continue to affect global trade. Even at the time of writing this article, Hamas recently launched a large-scale attack against Israel, which is very likely to completely break down relations between several countries in the Middle East. As a result, we’re already seeing global oil prices rising, and this will probably continue rising as this conflict further develops.
A scenario such as the Hamas-Israel conflict is unpredictable. But it highlights that businesses need to be ready for when the worst-case scenarios happen. This article looks into supply chain disruption examples to help you identify if your supply chain has any weak spots.
What is a supply chain disruption?

A supply chain disruption is a significant disturbance or interruption in the usual progression of goods, services, information, or resources within a supply chain.
Supply chains are intricate networks encompassing the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products, starting from suppliers and extending through manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, ultimately reaching consumers. Disruptions in these networks can occur for various reasons and have far-reaching consequences.
But what are some common causes of supply chain disruptions?
Natural disasters
Events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, wildfires, and tsunamis can damage infrastructure, disrupt transportation, and impact the availability of resources, leading to supply chain disruptions.
Man-made disasters
Industrial accidents, acts of terrorism, labor strikes, and political instability can disrupt supply chains by causing disruptions in production, transportation, or distribution.
Supplier issues
Problems with suppliers, such as quality issues, production delays, financial instability, or bankruptcy, can disrupt the supply of essential materials or components.
Transportation issues
Problems with transportation infrastructure, such as port congestion, strikes by transportation workers, fuel shortages, or disruptions in shipping routes, can delay the movement of goods.
Demand volatility
Rapid shifts in consumer demand, market trends, or unexpected spikes in orders can strain supply chains and lead to shortages or excess inventory.
Inventory shortages
Issues related to inventory management, such as stockouts, overstocking, or inaccurate demand forecasting, can disrupt the flow of goods.
Regulatory changes
Changes in government regulations, customs procedures, trade policies, or safety standards can impact supply chain operations and require adjustments to comply.
Cyberattacks
Cybersecurity breaches, including ransomware attacks or data breaches, can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive information, and disrupt supply chains.
State of Inventory Management: A Review of Rising Costs
Businesses worldwide have faced challenges from supply chain volatility and may continue to experience hardships going into 2024. Download the report and see how omnichannel selling has helped Katana customers increase sales orders despite economic uncertainty.
8 Real-life supply chain disruption examples
Now that you understand the types of events that cause the most severe supply chain delays let’s now look into real-life use cases where this has happened in the last four years.
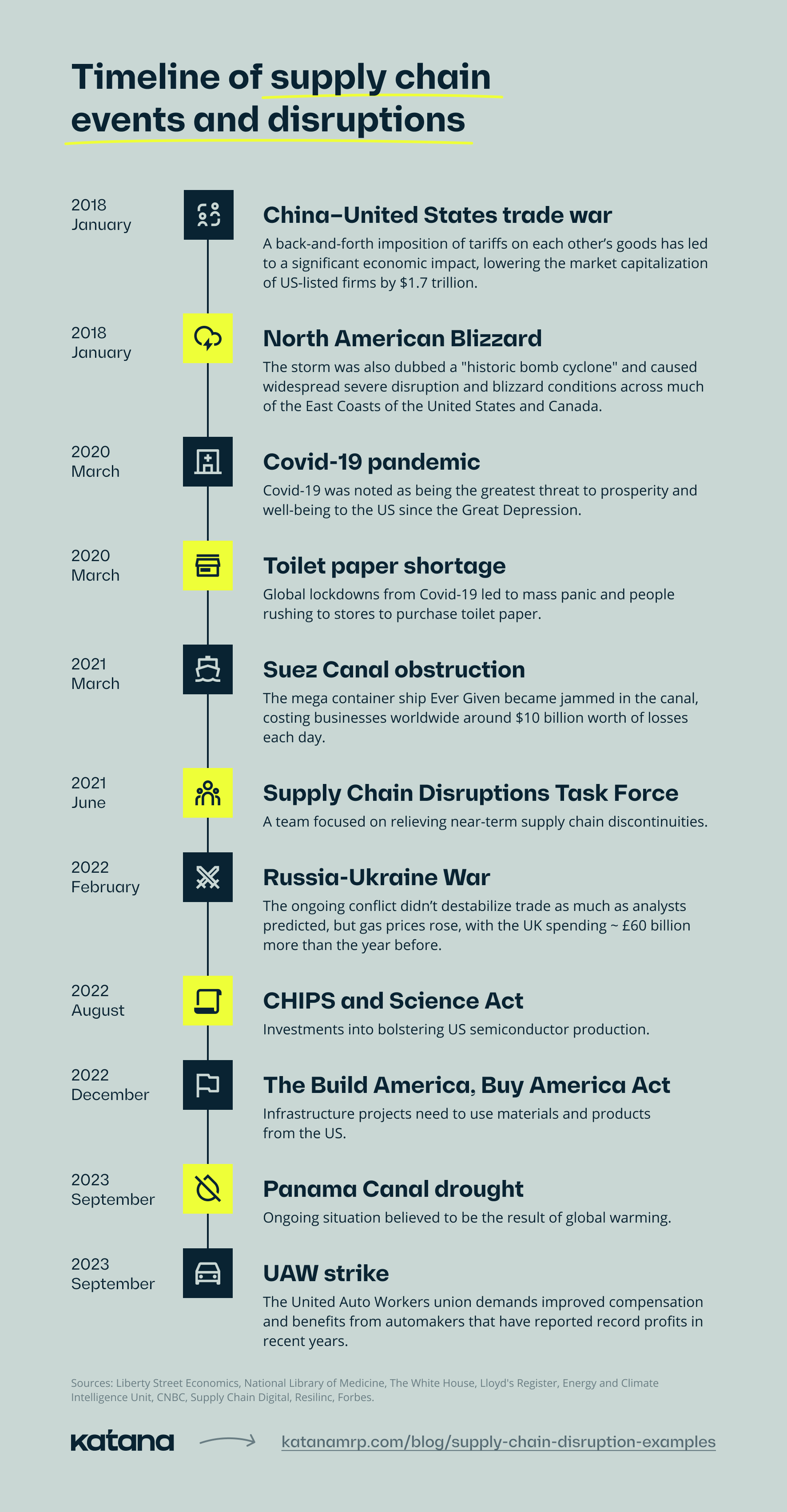
1. China–United States trade war
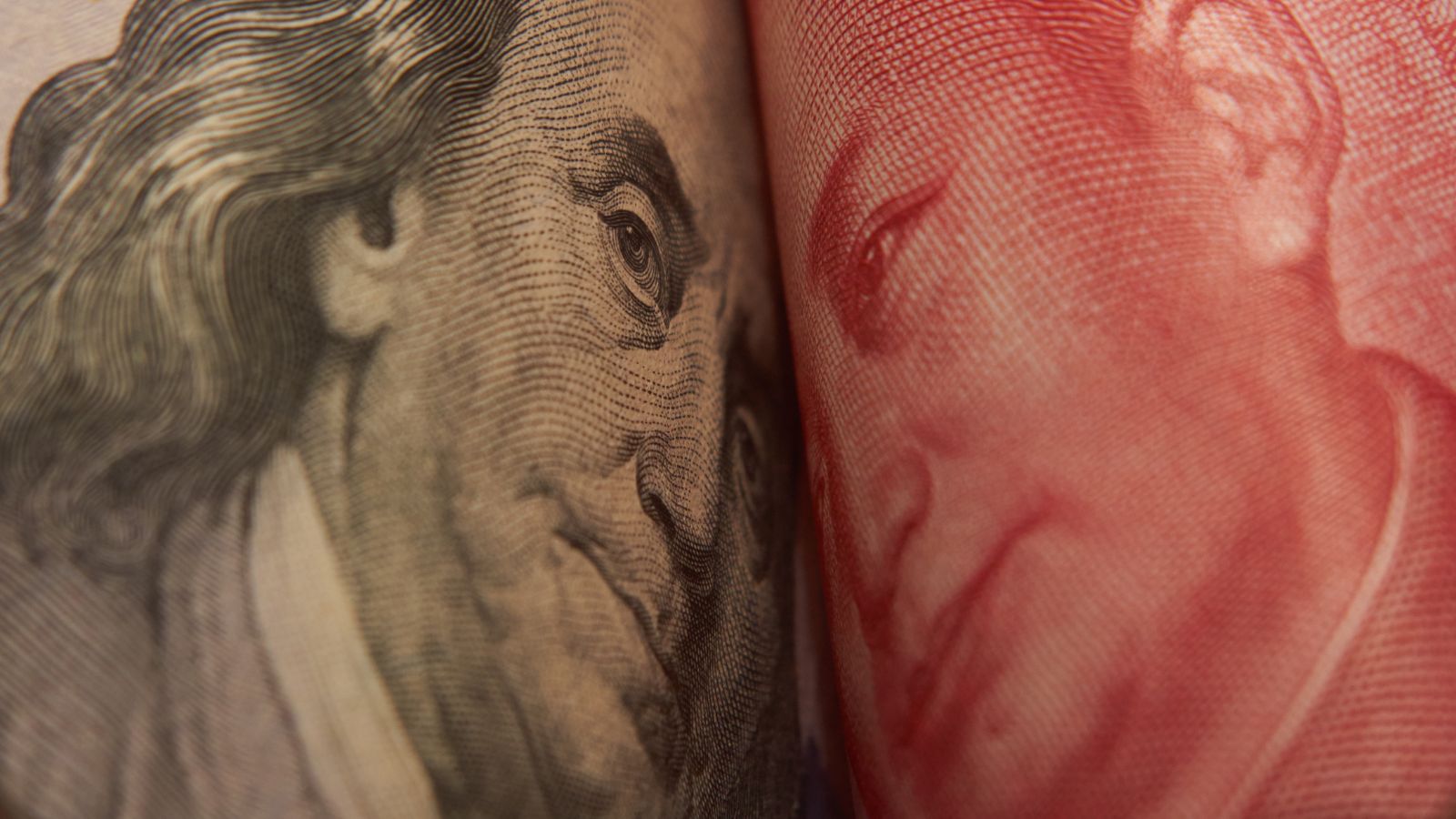

The China–United States trade war is a series of escalating trade tensions and tariffs imposed between the US and China, two of the world’s largest economies. It began in early 2018, imposed by the Trump administration, and is still in progress under the Biden administration, although there have been periods of negotiation and temporary truces.
2. North American Blizzard
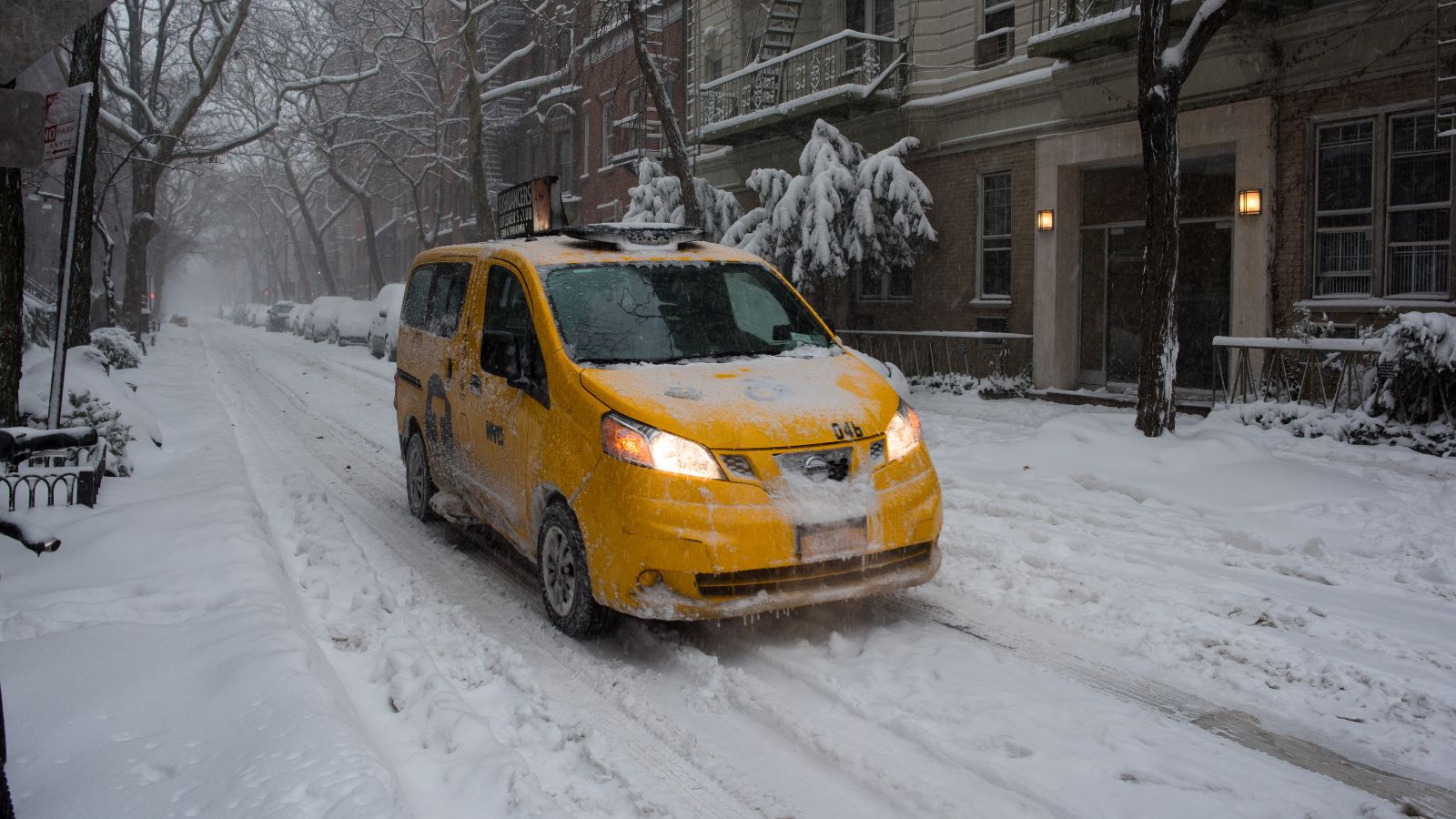

The North American Blizzard refers to a significant winter storm that affected parts of the eastern US and Canada in early January 2018. This bomb cyclone caused widespread travel Disruptions, including flight cancellations and delays, road closures, and hazardous driving conditions. Many schools and businesses were closed due to the weather.
3. Covid-19 pandemic
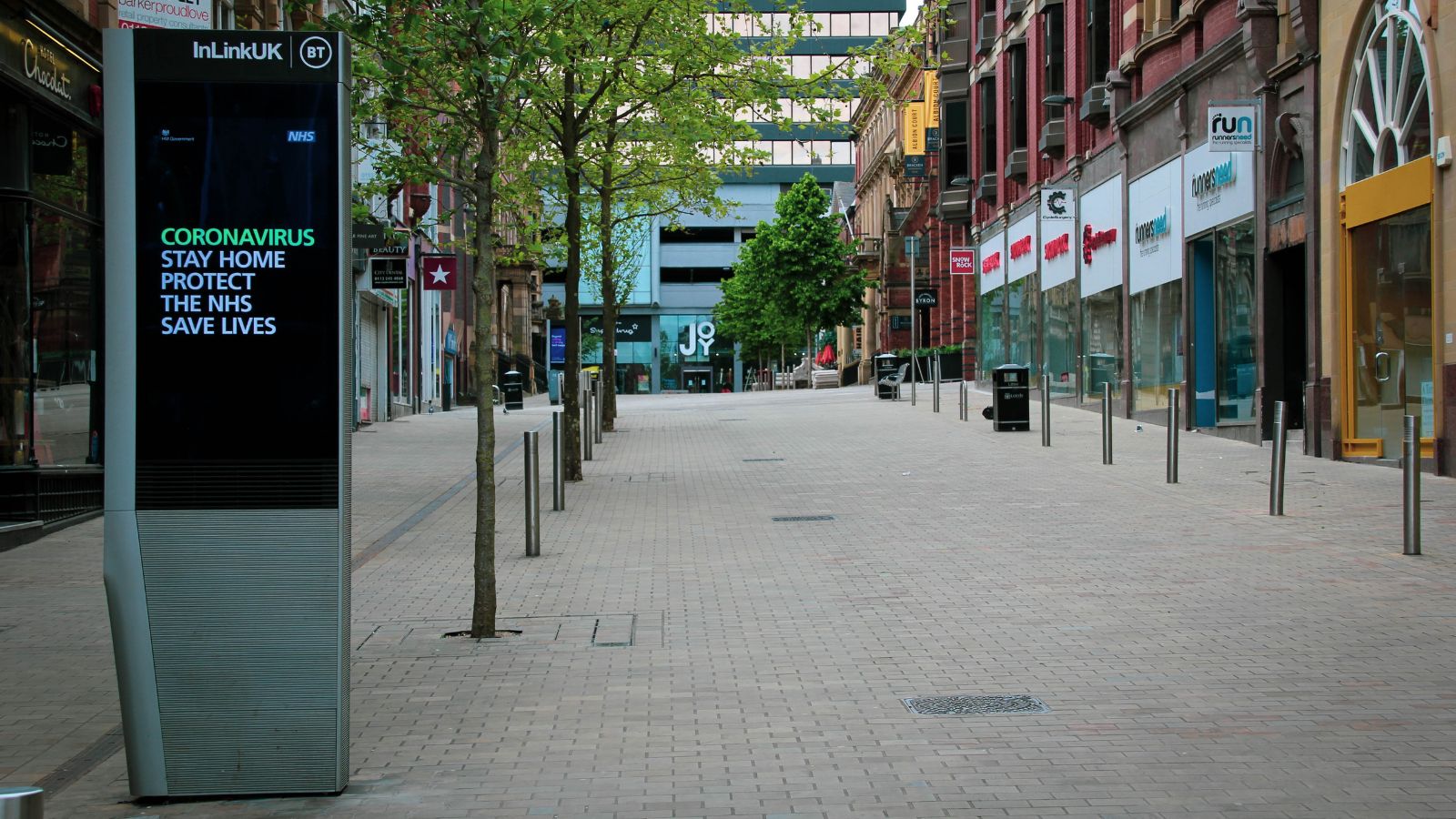

The Covid-19 pandemic had a profound and widespread impact on global supply chains, causing a range of supply chain issues and disruptions. Here are some of the ways in which Covid-19 contributed to these challenges. In the early stages of the pandemic, lockdowns led to:
- Factory closures and production disruptions
- Transportation and logistics
- International trade restrictions
- Uncertainty and demand volatility
Many businesses have reconfigured their supply chain strategies, invested in digital technologies, and implemented risk mitigation measures to better prepare for future disruptions. However, the pandemic highlighted the need for greater supply chain agility and flexibility in an increasingly interconnected global economy.
4. Toilet paper shortage

The toilet paper shortage was due to Covid-19, but it is a good case study of how mass hysteria can lead to supply chain issues.
A widespread surge in consumer demand for toilet paper led to empty store shelves and shortages in many parts of the world, particularly in the US and other Western countries, exacerbated by panic buying and production challenges.
5. Suez Canal obstruction
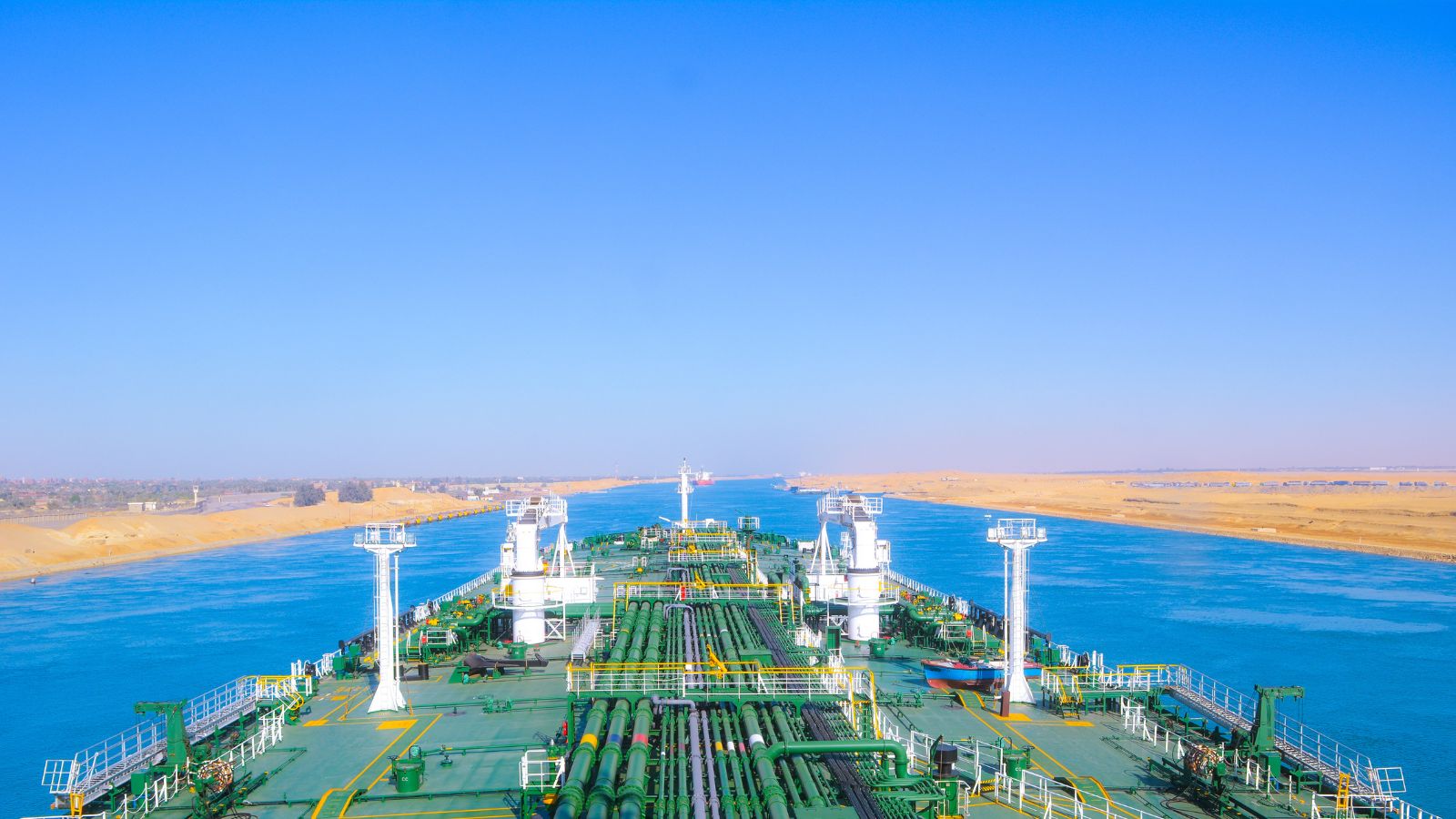

In March 2021, a large container ship named the Ever Given ran aground and became lodged sideways in the Suez Canal, one of the world’s most critical maritime trade routes. The incident resulted in the blockage of the Suez Canal for nearly a week, disrupting global trade and causing significant economic and logistical impacts.
The blockage of the Suez Canal disrupted the flow of goods, leading to a massive backlog of ships waiting to enter or exit the canal. It caused delays in the delivery of goods, increased shipping costs, and concerns about shortages of various products.
6. Russia-Ukraine War
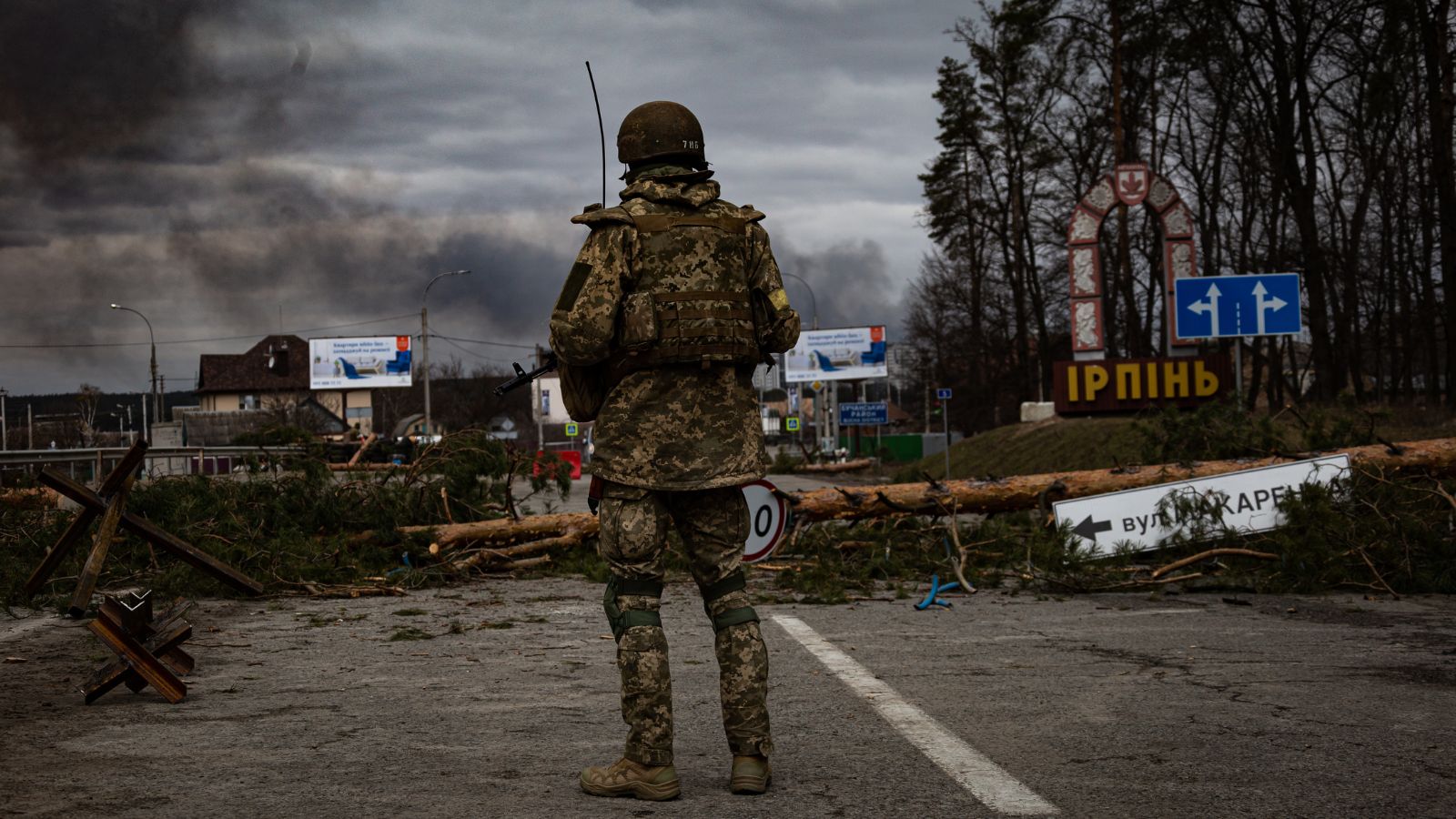

The conflict has constrained the availability of crucial metals previously imported from Russia in the US.
To illustrate, a substantial portion of key materials, such as 30% of platinum group elements, 13% of titanium, and 11% of nickel, which were formerly sourced from Russia, are no longer accessible. This situation has had a notable impact, particularly in sectors where these metals play a pivotal role.
For instance, nickel is a fundamental component in producing batteries used in automobiles and electronic devices. As a result of these shortages, there have been disruptions in the manufacturing of essential products. Similarly, the scarcity of titanium has raised significant concerns due to its status as one of the strongest metals employed in fabricating a wide range of industrial goods.
7. Panama Canal drought
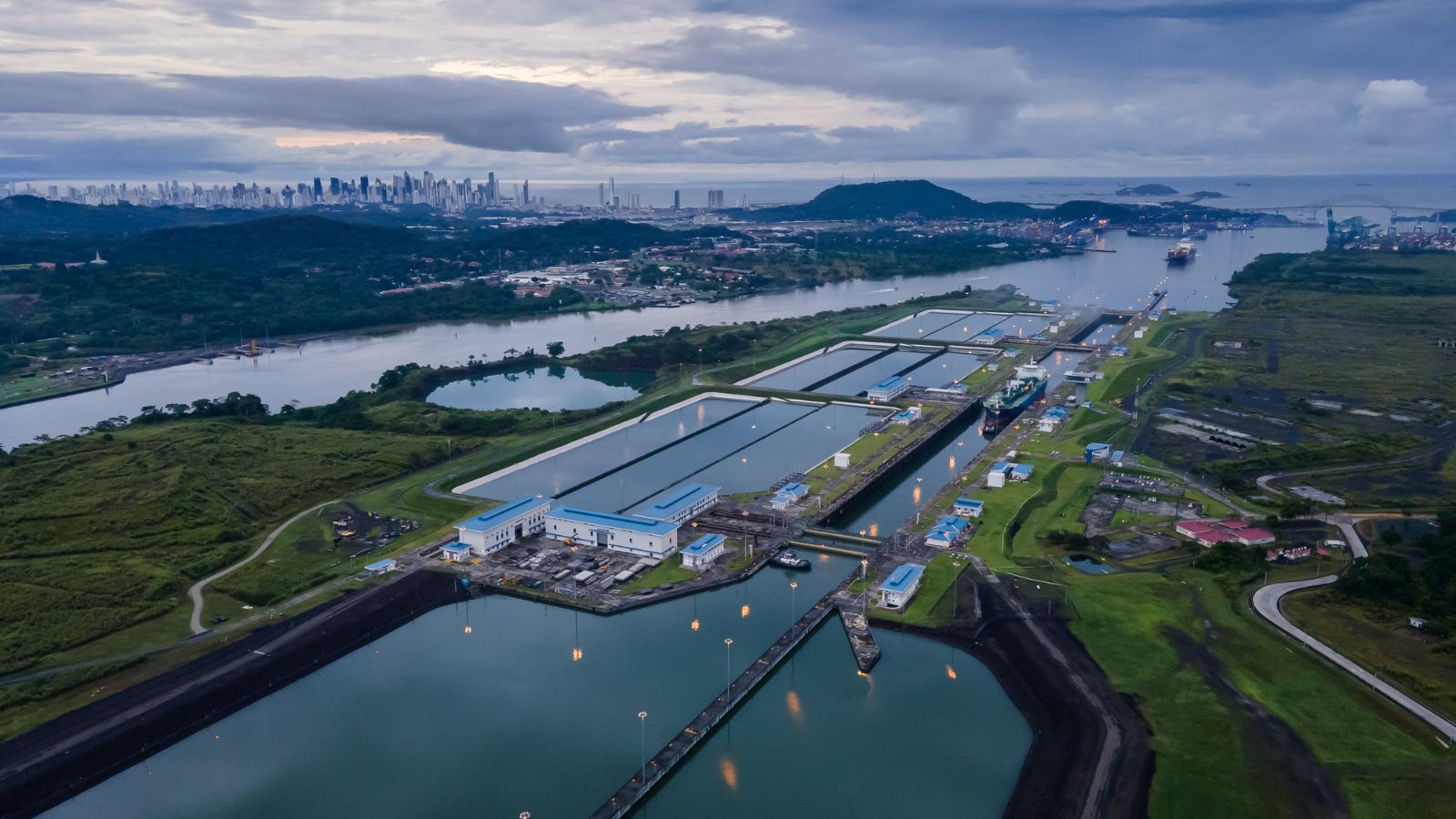

Climate-induced extreme weather events are placing significant stress on major shipping routes, and the potential onset of El Niño threatens to exacerbate this situation. The Panama Canal is grappling with water shortages, and Danish company Maersk has pointed to climate-related risks. El Niño, characterized by warming Pacific waters, has a gradual but far-reaching impact, contributing to the global temperature rise. Recent incidents like the Suez Canal mishap have underscored vulnerabilities in shipping, shining a spotlight on fragile supply chains.
8. UAW strike
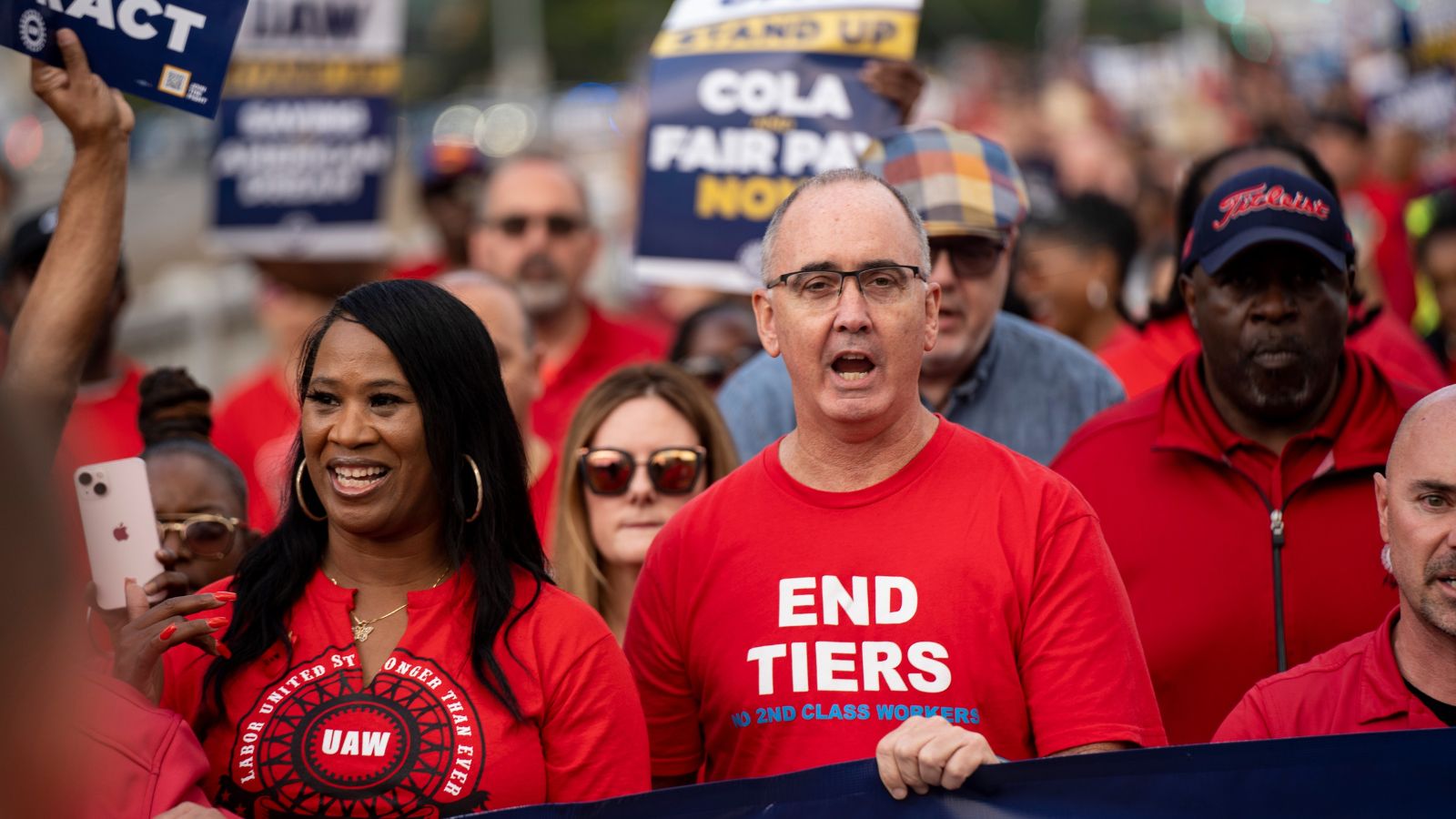

The UAW initiated negotiations with a request for a 40% salary increase over a four-year contract period.
The initial week of the strike incurred significant expenses. According to estimates from the Michigan-based economic consulting firm Anderson Economic Group LLC, the cumulative economic losses have now exceeded $1.6 billion. These losses have primarily been concentrated in a few regions where strike actions or workforce reductions have already taken place.
How is the US trying to address supply chain delays?

As mentioned earlier, governments (specifically the US) have been trying to set up initiatives to curb the threat posed by a weak supply chain. Here are just a few examples of those attempts.
Supply Chain Disruptions Task Force
The Task Force was created in June 2021 to tackle imbalances between supply and demand that became apparent in multiple industries as the economy started to recover following the Biden Administration’s significant vaccination and economic support initiatives.
CHIPS and Science Act
The CHIPS Act was signed into law on August 9, 2022, to enhance US competitiveness, foster innovation, and strengthen national security.
This legislation is geared towards stimulating investments in domestic semiconductor manufacturing capacity. Additionally, it aims to kickstart research and development and the commercialization of cutting-edge technologies, including quantum computing, artificial intelligence, clean energy, and nanotechnology.
The CHIPS Act intends to establish new high-tech hubs in various regions and promote the growth of a more diverse and inclusive science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) workforce.
The Build America, Buy America Act
The Build America, Buy America Act, incorporated into the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act on November 15, 2021, emphasizes the importance of prioritizing the utilization of services, goods, products, and materials made and available within the US by the federal government.
Using inventory management software to avoid supply chain delays
Automation is the key to controlling your inventory and avoiding supply chain delays.
Inventory management software provides tools and capabilities to optimize inventory levels, monitor demand and supply, and make more informed purchasing decisions. Here are several ways in which inventory management software can help mitigate the risks of supply chain disruptions:
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Demand forecasting
- Safety stock optimization
- Supplier and vendor management
- Omnichannel order automation
- Data insights and analytics
- And more
By leveraging these features and capabilities, inventory management software helps businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, streamline operations, and respond effectively to supply chain disruptions. This proactive approach can minimize the impact of disruptions and ensure that products are available when and where they are needed.
Want to see Katana in action? Book a demo to get all your questions answered regarding Katana’s features, integrations, pricing, and more.
We hope that you found this article useful, and if you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.

James Humphreys
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty with Katana Cloud Inventory — AI-powered for total inventory control