1 in 2 customers prefer a real human over an AI chatbot when chatting online

Customer service is one of the most popular use cases for generative AI.
Tools like GTP-4 or Google Bard are disrupting B2C interactions, and businesses in virtually every industry have implemented solutions like AI chatbots into their customer-facing operations. These bots can handle complex queries, provide information, and reduce the workload of customer service representatives. A recent study conducted by Katana showed that 94% of SMB ecommerce merchants intend to incorporate AI into their business operations in 2024.
But is that what customers want?
To gauge people’s opinions on the effectiveness of AI chatbots, we ran a survey using Pollfish and asked people detailed questions about their interactions with AI tools. Are these artificial intelligence tools really delivering on their promise to elevate the customer experience? Here’s what our analysis revealed.
Key findings
- 1 in 2 customers prefer talking to a person over an AI chatbot
- Millennials and Gen Zers are more comfortable sharing information with AI compared to older generations
- High-income respondents are more satisfied with AI chatbots, yet they still prefer human interaction
- Men are more trusting than women when it comes to sharing information with AI chatbots
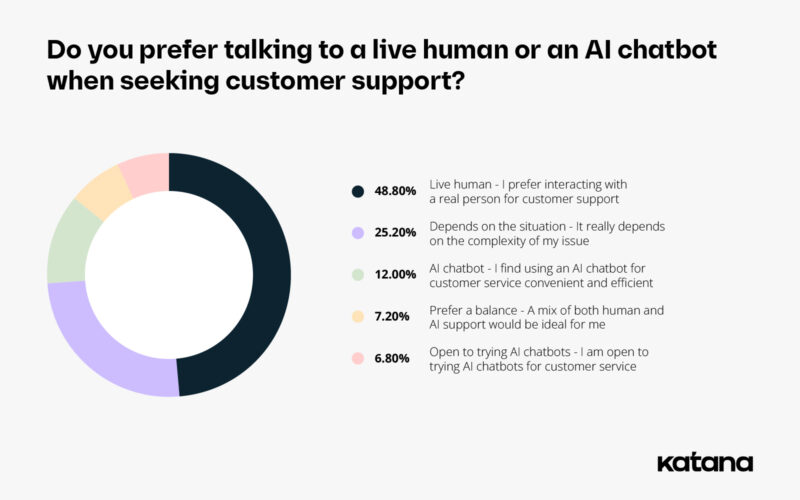
Humans vs. AI chatbots: 1 in 2 customers prefer a person
Generally speaking, the results of our survey are clear: even in the age of AI and digital transformation, people still prefer talking to a human rather than interacting with a chatbot.
Roughly 49% of respondents said they prefer interacting with a real person for customer support, while only 12% said they prefer interacting with an AI chatbot. At the same time, 25% of respondents said that it depends on the situation and the complexity of their issue. AI chatbots are effective when it comes to quick, less complex issues, but the more complex the situation, the higher the preference for human interaction.
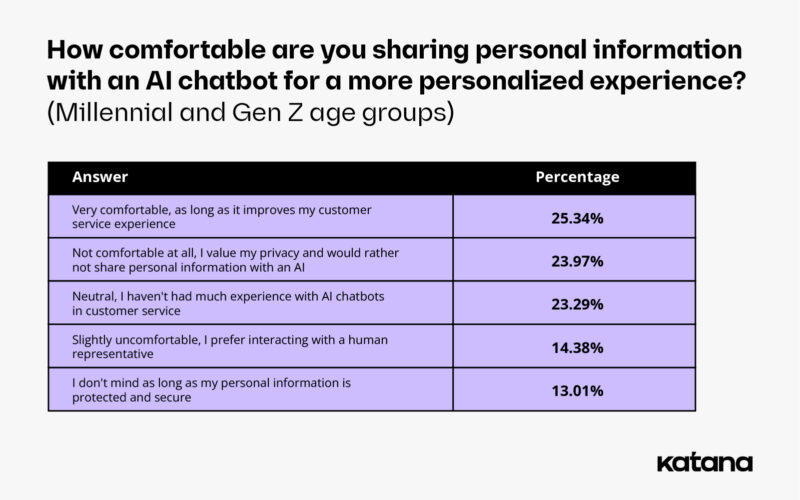
Millennials and Gen Zers are more comfortable sharing information with AI compared to older generations
Looking at how respondents in different age groups responded to our survey, we notice that younger generations are more trusting of artificial intelligence services.
25% of Millennials and Gen Zers said they are very comfortable sharing personal information with AI chatbots for a more personalized experience, while 24% said they were uncomfortable with it. 23% of younger respondents said they don’t have much experience interacting with AI for customer service, and 13% don’t mind sharing information with a chatbot if they know that information is protected and secure.
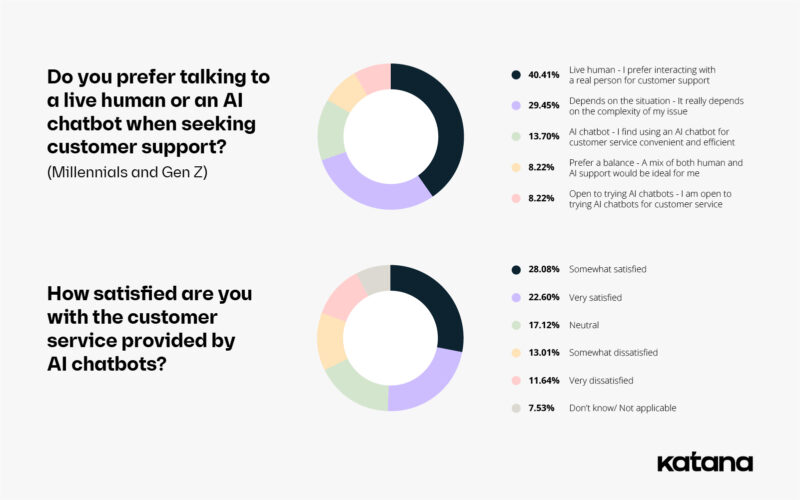
However, 40% of our Millennial and Gen Z respondents said they prefer interacting with a live human for customer support, with only 13% picking AI interaction. This shows that while younger generations are quite open and trusting when it comes to interacting with chatbots, they still prefer talking to an actual person.
Moreover, most of these respondents (28%) said they were only ‘somewhat satisfied’ with the customer service provided by chatbots, so it’s clear there is still room for improvement in this area.
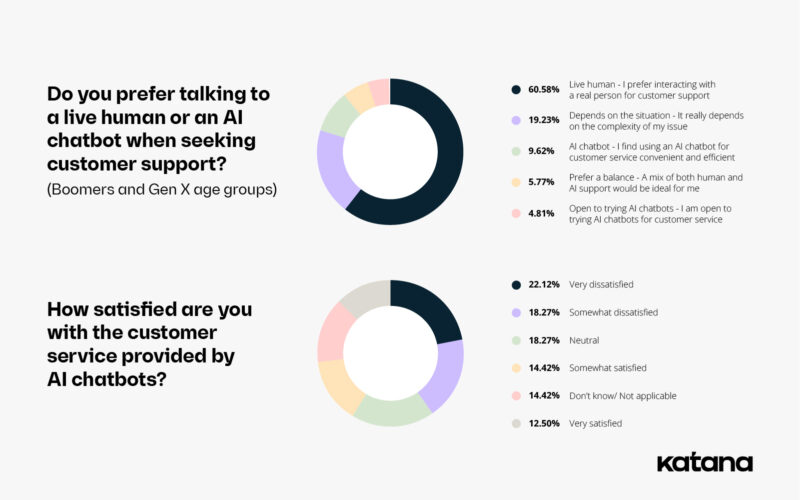
While younger generations are relatively open when interacting with and sharing information with chatbots, older generations are much more skeptical and reserved. 38% of Boomers and Gen Xers said they felt very uncomfortable sharing their personal information with a chatbot. Only 22% of respondents over the age of 45 said they were comfortable sharing such information with AI.
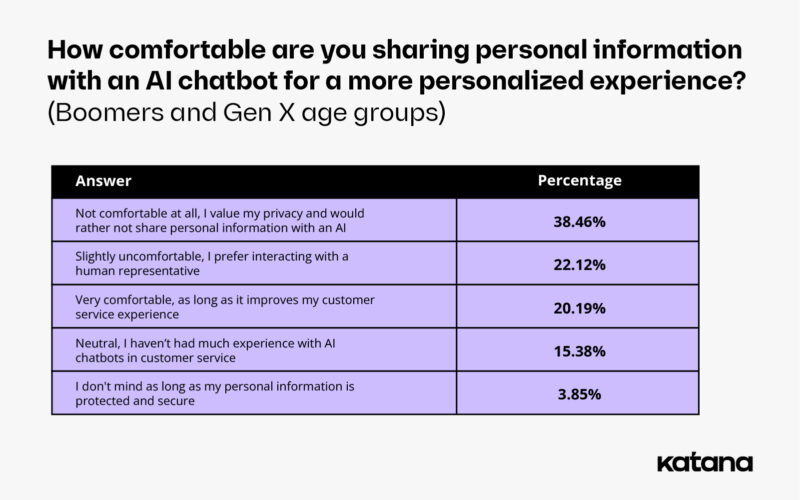
When it comes to customer support interactions, 61% of Gen X and Boomer respondents said they prefer talking to an actual person, with only 9% saying they prefer interactions with chatbots. 22% of respondents in these age groups also said they were very dissatisfied with the level of customer service provided by AI chatbots.
High-income respondents are more satisfied with AI chatbots, yet they still prefer human interaction
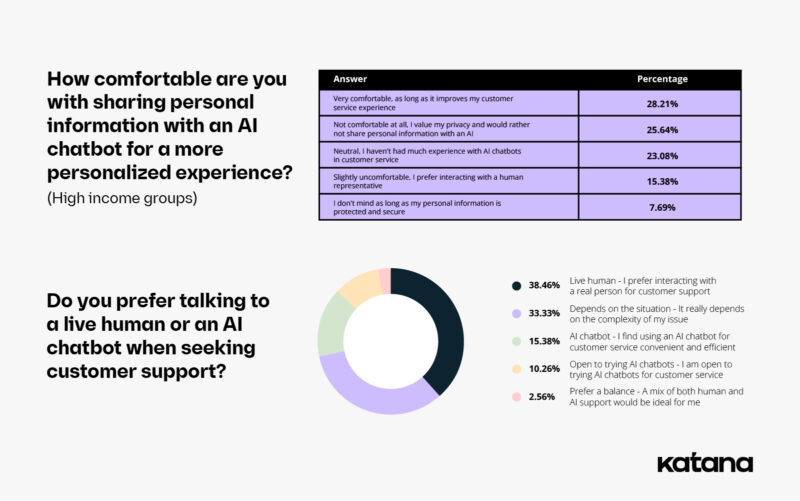
To get an even more detailed picture of how customers feel about AI chatbots, we decided to look at how respondents in different income groups responded to our survey. As it turns out, the higher the revenue, the higher the satisfaction with artificial intelligence: 28% of high-income-earning respondents said they were very satisfied with the customer service provided by AI chatbots, with 10% saying they were very dissatisfied.
However, while the majority of respondents in this income group (28%) said they were very comfortable sharing personal information with chatbots, 26% said they were very uncomfortable doing so. Moreover, 38% of high-income respondents still prefer talking to a live human for customer support, and only 15% prefer a chatbot.
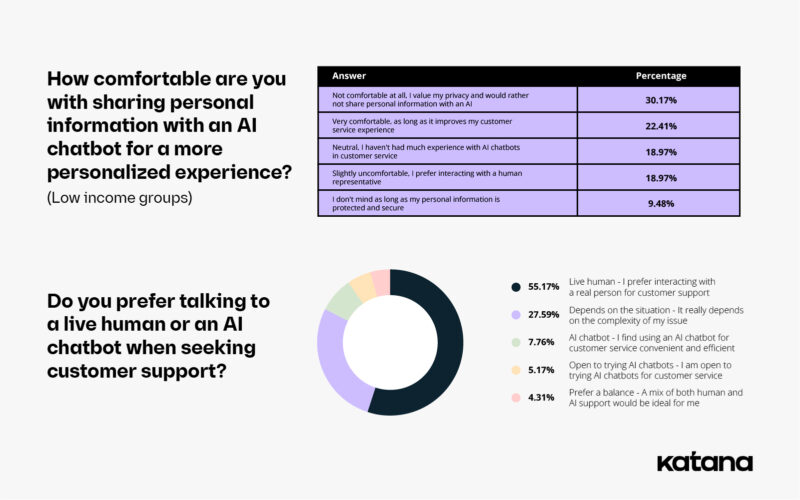
By comparison, 30% of those in the low-income group said they were not comfortable at all sharing sensitive information with AI. 55% of these respondents also said they preferred talking to a live human for their customer service needs, with only 8% choosing an AI chatbot.
Men are more trusting than women when it comes to sharing information with AI chatbots
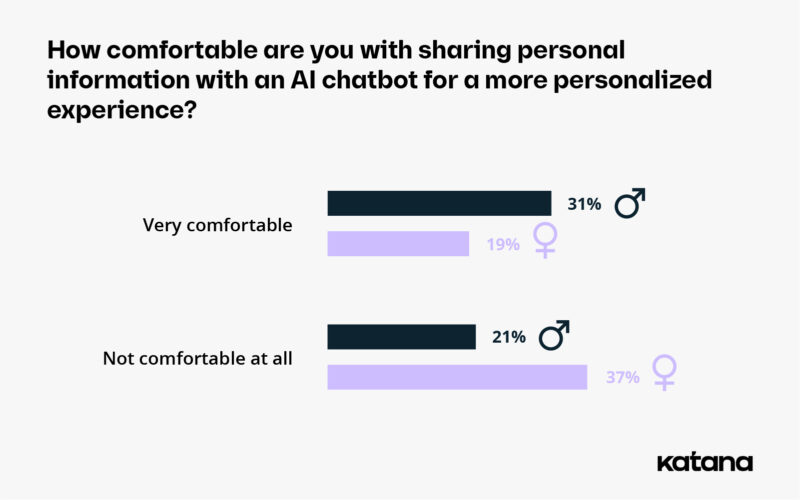
Looking at the results of our survey in terms of gender, we notice that female respondents are more cautious and less trusting than male respondents when it comes to sharing personal information with artificial intelligence tools.
31% of male respondents said they were very comfortable sharing information with AI, compared to only 19% of women. In fact, most of our female respondents (37%) said they were uncomfortable sharing this type of information with chatbots.
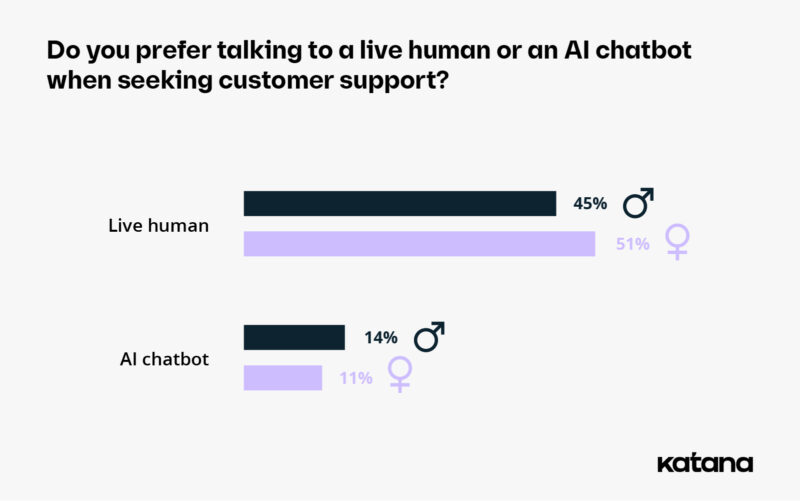
However, there’s something that both genders agree on: 51% of women and 45% of men said they prefer talking to a real person over a chatbot for their customer support needs.
Final takeaway: business owners, know your audience!
Our survey reveals that there are clear differences in preference related to age, income, and gender that guide people’s interaction and openness towards artificial intelligence services. The main lesson business owners can take from this is: know your audience.
Before implementing artificial intelligence tools to streamline your customer support services, take a close look at your target audience. Factor in things like age, income, gender, and other potential relevant characteristics specific to your business in your decision-making process. This way, you’ll make sure that the AI-related tools you adopt don’t end up alienating your customers.
Methodology
This report is based on a Pollfish survey gauging people’s opinions on the use of artificial intelligence in customer service. We surveyed 250 respondents across Canada and the U.S., aged 18 through 50+, and asked them detailed questions regarding the use of AI chatbots in customer service to generate the results featured in this report.

Ioana Neamt
Table of contents
Get inventory trends, news, and tips every month
Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty with Katana Cloud Inventory — AI-powered for total inventory control