What is a manufacturing execution system (MES)

Once upon a time, there was a company called Handy Trinkets. They started in a small garage, making bespoke widgets that quickly became a hit. At first, keeping track of what to make, when, and how was easy. The team was small, and a big whiteboard with sticky notes was enough for planning everything from ordering materials to shipping finished widgets.
As Handy Trinkets grew, things got complicated. Orders poured in, the team expanded, and the self-proclaimed kanban board couldn’t keep up. Suddenly, they found themselves juggling dozens of orders, materials arriving at different times, machines needing maintenance, and products that needed to be just right to keep customers happy. It was like trying to conduct an orchestra without knowing how to read music.
Amid this chaos, the team realized they needed help. They spent too much time figuring out what to do next instead of actually making their beloved trinkets. They needed a way to see everything happening in real time, from the arrival of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. And not just see it, but manage it effectively to avoid delays, reduce waste, and ensure every widget is perfect.
This article is all about manufacturing execution systems (MES), how they work, what are the benefits, and a great deal more.
Table of contents
- What is an MES system?
- Benefits of MES
- Core MES features
- How do MES systems relate to other systems?
- MES vs. ERP vs. MRP: What’s the difference?
- MES and ERP integration
- Variations on the shop floor
- How does MES help to eliminate variations?
- Is a manufacturing execution system right for your business?
- The future of MES
- Cloud inventory software that does everything an MES does and more
What is an MES system?
Manufacturing execution systems are computerized control systems to manage and optimize production on the shop floor. MES systems monitor and control manufacturing operations and information flow on your shop floor.
In other words, an MES system helps to track and record the transformation of raw materials to finished goods on the shop floor. This allows manufacturers to control all activities and operations on their shop floor. An MES aims to ensure the effective execution of production operations and improve output.
MES has real-time features to help you control all aspects of your shop floor, including:
- Inventory
- Workers
- Machines
- Support services
Along with handling your shop floor operations, MES can help you with:
- Shop floor planning
- Managing the entire product lifecycle
- Production tracking
- Order management
- Manufacturing data analysis
- Product traceability

Benefits of MES
Manufacturing execution systems offer a wide range of short- and long-term benefits. So, let’s go over the benefits of using this software within your business.
1. Reduce costs
MES allows you to track costs in real time from the shop floor, such as:
- Labor
- Downtime
- Maintenance
This data at hand will help you increase productivity and minimize your manufacturing costs. A better understanding of your expenses helps your business make informed decisions and identify saving opportunities.
2. Minimize inventory
MES provides information about the materials and products you need on hand. That makes keeping your inventory levels optimal and reducing your carrying costs easy. With a real-time view of your inventory levels, you also know precisely what you need to reorder and when.
3. Reduce waste
Easily identify inconsistencies on your production lines, so you can immediately halt them to limit the number of faulty products or manufacturing waste that appears on the shop floor. MES helps you achieve this through:
- Full traceability of your raw materials, production, and fulfillment
- More reliable and precise process planning
- Data-based operational and strategic decisions
4. Eliminate paperwork
It’s not just a dream — paperless manufacturing is a reality. Adopting a manufacturing execution system eliminates paperwork and manual data-entry processes from your daily operations. Using an MES allows you to improve your production efficiency effortlessly.
Core MES features
MES system is clearly a quite complex piece of software with a ton of features to manage anything related to manufacturing. But let’s look at some of the core features a manufacturing execution system has:
- Collecting data — Collect valuable information on your production lines to improve your manufacturing processes.
- Labor management — Easily manage your staff, overall equipment effectiveness, and other resources from the shop floor to maximize their utility.
- Product traceability — Effortlessly track the progress of your products and see the status of operations in real time.
- Quality control — An MES makes it easy to follow your quality control checklist for improved quality control, helping to address production variations and enhance product quality.
- Performance analysis — As you can see the entire production process, you can quickly identify areas of your production that are lacking in productivity.
- Maintenance management — Perform predictive maintenance to avoid hindering or stopping your production flow.

How MES systems relate to other systems?
An MES helps a product developer manage the actual manufacturing of a product and collect, store, and make production data available for the entire manufacturing process.
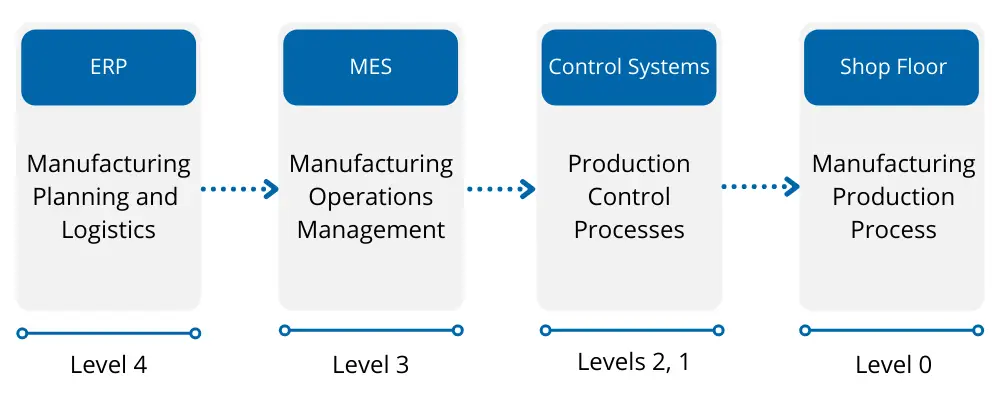
However, MES doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s part of a complex system of levels that allows you to ensure your manufacturing processes are optimized for maximum efficiency and productivity. Smart manufacturing is underpinned by the ISA-95, the international standard for developing automation in manufacturing between enterprise and control systems, based on the Purdue Reference Model for CIM (hierarchical form).
Within this, a manufacturing execution system is a level 3 system, otherwise known as a manufacturing operations management system (MOMS).
It can receive and send information to level 4 systems, such as an ERP software responsible for manufacturing planning and logistics. Level 1 and 2 systems control production processes, including continuous and discrete control and batch automation systems to track production. Finally, level 0 refers to physical manufacturing production at your shop floor level.
Having all these systems communicating and working together is vital to increase your productivity.

MES vs. ERP vs. MRP: What’s the difference?
ERP, MES, and MRP can share a lot of functionality, but they all have a specific role to fill. Let’s go over the differences between these systems.
ERP is like the backbone of the company’s operations, handling the big-picture tasks. It creates and manages basic production schedules, material use, deliveries, and shipments and gathers all sorts of information about your business.
It also dives into inventory management, order management, accounting, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM). Think of ERP as the conductor, ensuring all parts of the business are in sync, from the front office to the factory floor.
MES, on the other hand, zooms in on the shop-floor manufacturing operations. It’s all about managing and reporting on production line activities in real time. MES is the section leader for the manufacturing process, ensuring each instrument (or machine) and musician (or worker) performs optimally, notes are played correctly (quality control), and the piece is performed on time (production scheduling).
Then there’s MRP, which focuses on the planning, scheduling, and inventory control of the manufacturing process. MRP is like a meticulous composer, deciding which notes need to be played (materials needed) and when (timing) to ensure the music (production) flows smoothly without interruption.
As technology advances, the boundaries between ERP, MES, and MRP systems may continue to blur, but each system’s unique focus remains its strength. The key is understanding how they complement each other, ensuring a harmonious performance that leads to efficient production and a successful business.
MES integrations
If you’re already set up with an ERP or material requirements planning system, you may be wondering if MES can work with your other systems.
If your system isn’t already performing the tasks that all three systems need to achieve, here’s how MES systems can benefit your other software.
MES and ERP
With your ERP tools, you can prepare your operations, from schedules to deliveries needed, and with your MES systems, you can monitor the progress of jobs from the floor level.
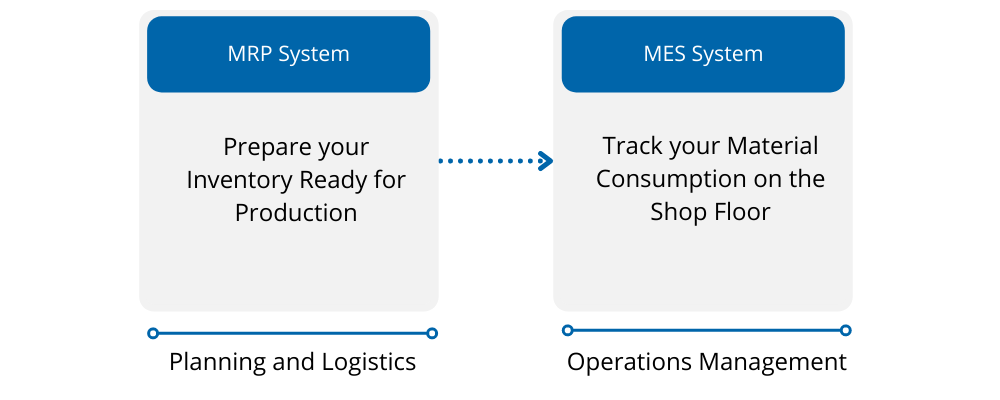
MES and MRP
Your MRP is going to help you prepare your inventory for production, and your MES will help you track your raw material consumption on the shop floor.

Variations on the shop floor
A manufacturing execution system will be one of the most important tools in your arsenal for controlling and managing your shop floor scheduling.
There can be a high level of variation on your shop floor so it presents a great opportunity for you to find areas of your manufacturing operations to optimize and improve production. Knowing the variations that can appear on the shop floor will allow you to use your MES to mitigate these issues. But what are the shop floor variations?
Common cause
Common variations are a part of the process, such as natural wear and tear, old machinery breaking down, and other expected factors.
Special cause
Special variations are unexpected issues, like something external to your production lines. Special variations include:
- An operator making a mistake
- Parts breaking
- Power outages
This is why an MES is perfect for manufacturers using statistical process control to observe the performances of their processes to predict, identify, and remove these sources of variations. Let’s go over some of the ways an MES achieves this.
How does MES help to eliminate variations?
Let’s explore how an MES can help you identify and get rid of the issues causing product variations.
Real-time data
Having a real-time overview lets you detect problems immediately, make corrections, and minimize the faulty finished goods that enter circulation.
Shop floor control rules
MES solution allows you to detect out-of-control or non-random problems by setting rules highlighting issues on the shop floor.
Corrective actions
Once you have a system that can identify variations, you can then start implementing solutions, which can be things including:
- Training staff
- Process standardization
- Refining your processes
That’s everything you need to know about MES. But is MES the right tool for your business?
Is a manufacturing execution system right for your business?
MES systems are crucial for regulated industries dealing with perishable inventory. However, understanding how an MES system can benefit your business will depend on your needs and goals. Before choosing and using an MES, you need to ask yourself some questions.
What does your business need?
Understanding your business’ short- and long-term goals is vital before choosing to use any tools or systems. An MES system will allow you to improve your manufacturing operations — but what exactly are you looking to improve? Without a clear understanding of your goals, a management system will not bring you the benefits you seek. Spend time defining your goals and asking yourself what issues you want to solve.
This brings us to the next consideration.
What pain points can an MES solve?
Identifying your manufacturing challenges and pain points allows you to use the MES you choose to solve them. This may be removing bottlenecks from your production by providing real-time inventory updates or optimizing your shop floor operations through product bill of materials (BOM). Look at the benefits section for a complete overview of how an MES system can help your business.
Available integrations
The whole purpose of MES implementations is to work within a manufacturing structure integrated with other systems and tools to ensure full control of logistics, operations, and production and constantly improve processes.
That’s why you need to choose an MES that integrates with your other business tools. Choose an MES software with seamless integration into an ERP solution or MRP system to manage and improve your production planning and logistics, shop floor control, and manufacturing operations effortlessly.
The future of MES
The use of MES in manufacturing will change with new technological manufacturing trends such as Industry 4.0, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI).
These developments will enable MES to provide real-time visibility and control over the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished products. The use of smart sensors and predictive analytics will allow manufacturers to optimize production, minimize downtime, and improve quality control.
Additionally, MES will become more integrated with other enterprise systems, such as ERP and PLM, to provide a comprehensive view of the manufacturing operations and supply chain. The increasing demand for customization and personalization will drive the need for MES to be highly flexible and scalable to accommodate the changing needs of manufacturers.
Cloud inventory software that does everything MES does and more
Katana Cloud Inventory Platform offers everything an MES system for manufacturing offers but adds additional features as well, so you can get it all done with the same platform. Katana lets businesses:
- Manage all four types of inventory — finished products, raw materials, work-in-progress, MRO
- Plan and schedule production
- Manage your shop floor
- Analyze your sales performance
- Forecast and plan inventory
- And much more
In addition, Katana integrates with a ton of business tools, including QuickBooks Online, Shopify, Xero, and BigCommerce, allowing you to effortlessly sync your data across all your platforms.
Request a demo today to see for yourself how Katana can benefit your business.
Manufacturing execution system FAQs
What is MES?
A manufacturing execution system (MES) is a specialized software solution designed to manage and monitor the manufacturing process on the shop floor. It serves as a bridge between the factory floor operations and the higher-level planning systems, ensuring that manufacturing is executed efficiently, products meet quality standards, and resources are optimally utilized.
What does a manufacturing execution system do?
An MES oversees the entire manufacturing process from start to finish. It tracks real-time data on production operations, manages workflows, ensures quality compliance, and provides insights into machine performance and product lifecycle. By doing so, it helps reduce waste, minimize downtime, and enhance productivity, making sure that the manufacturing process aligns with the planned output.
How does a manufacturing execution system work?
An MES works by collecting data in real time from machines, devices, and personnel on the shop floor. It uses this data to monitor production progress, ensure that processes run within predefined parameters, and identify bottlenecks or issues as they arise. The system can adjust workflows, allocate resources effectively, and provide decision-makers with insights through detailed analytics and reporting. For businesses aiming to enhance their manufacturing operations, incorporating an MES can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, product quality, and time to market.
What is the difference between MES and ERP?
While MES focuses on the shop floor’s day-to-day operations, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have a broader scope, managing company-wide resources and business processes. ERP integrates various business functions such as accounting, HR, inventory, and customer relations, offering a macro view of the organization’s operations. In contrast, MES provides a micro view that’s specific to manufacturing, often working within the framework set by ERP systems. For those looking to streamline not just manufacturing but also broader business processes, exploring solutions like Katana, which offers smart manufacturing software with integrated ERP features, could be beneficial.
More on manufacturing










